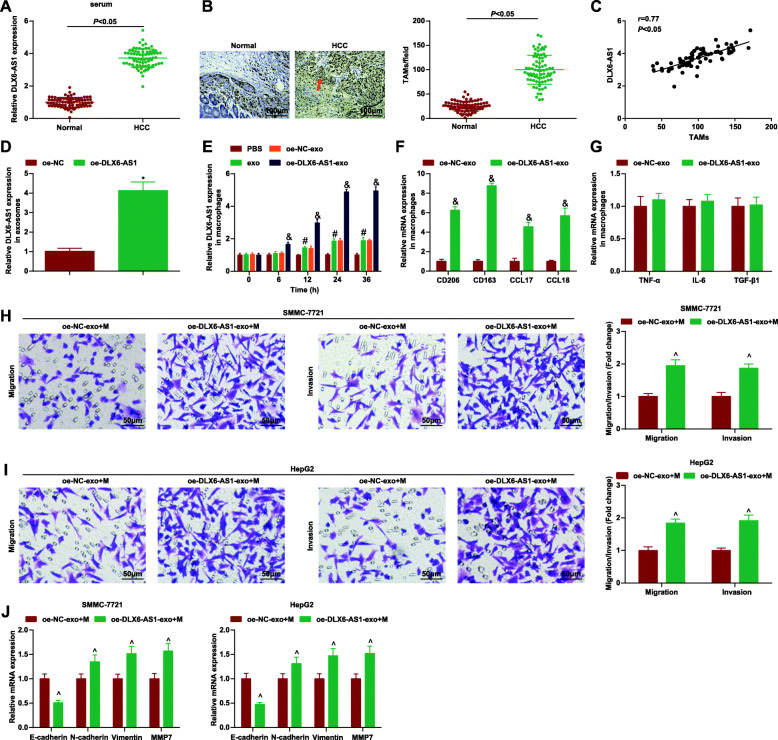
Fig. 4.
DLX6-AS1 from HCC-exo stimulates M2 macrophage polarization to accelerate migration, invasion and EMT in HCC. a. RT-qPCR detection of DLX6-AS1 expression in serum of HCC patients and healthy controls; b. Detection of CD68 expression in clinical samples through immunohistochemical staining; c. Correlation between expression of DLX6-AS1 and CD68 was analyzed using Pearson test; d. RT-qPCR detection of DLX6-AS1 expression in HCC-exo delivering oe-DLX6-AS1; e. RT-qPCR detection of DLX6-AS1 expression in macrophages after co-culture with HCC-exo delivering oe-DLX6-AS1; f. RT-qPCR detection of M2 macrophages markers (CD206, CD163, CCL17 and CCL18) after co-culture with HCC-exo carrying oe-DLX6-AS1; g. RT-qPCR detection of M1 macrophages markers (TNF-α, IL-6 and TGF-β) after co-culture with HCC-exo carrying oe-DLX6-AS1; h. Transwell assay tested the migration and invasion of SMMC-7721 cells after co-culture with M2 macrophages induced by HCC-exo carrying oe-DLX6-AS1; i. Transwell assay tested the migration and invasion of HepG2 cells after co-culture with M2 macrophages induced by HCC-exo delivering oe-DLX6-AS1; j. RT-qPCR of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, vimentin and MMP7 mRNA expression in SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cells after co-culture with M2 macrophages induced by HCC-exo delivering oe-DLX6-AS1; data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (repetition = 3) and evaluated by One-way AVONA and Tukey’s test. * P < 0.05 compared with the oe-NC group; # P < 0.05 compared with the PBS group; & P < 0.05 compared with the oe-NC-exo group; ^ P < 0.05 compared with the oe-NC-exo + M group