Figure 1.
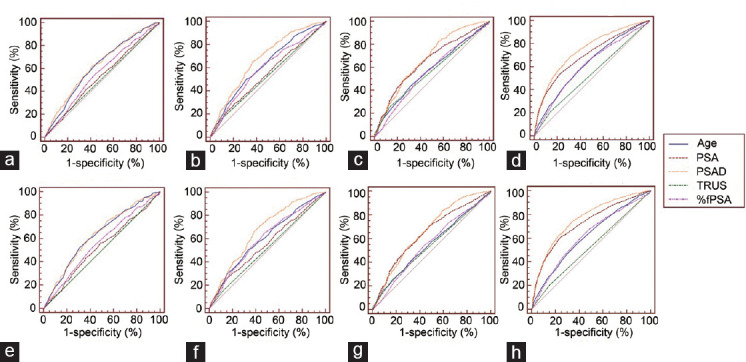
Diagnostic efficacy of PSAD. The comparison of diagnostic efficacy of age, PSA, PASD, TRUS, and %fPSA for PCa in patients (a) with PSA levels ranging from 4.0 ng ml−1 to 10.0 ng ml−1, (b) with PSA levels ranging from 10.1 ng ml−1 to 20.0 ng ml−1, (c) with PSA levels above 20.0 ng ml−1, and (d) regardless of PSA levels. The comparison of diagnostic efficacy of age, PSA, PASD, TRUS, and %fPSA for HGPCa in patients (e) with PSA levels ranging from 4.0 ng ml−1 to 10.0 ng ml−1, (f) with PSA levels ranging from 10.1 ng ml−1 to 20.0 ng ml−1, (g) with PSA levels above 20.0 ng ml−1, (h) regardless of PSA levels. PCa: prostate cancer; HGPCa: high-grade prostate cancer; PSA: prostate-specific antigen; PSAD: prostate-specific antigen density; TRUS: transrectal ultrasound; %fPSA: the ratio of free-to-total PSA.
