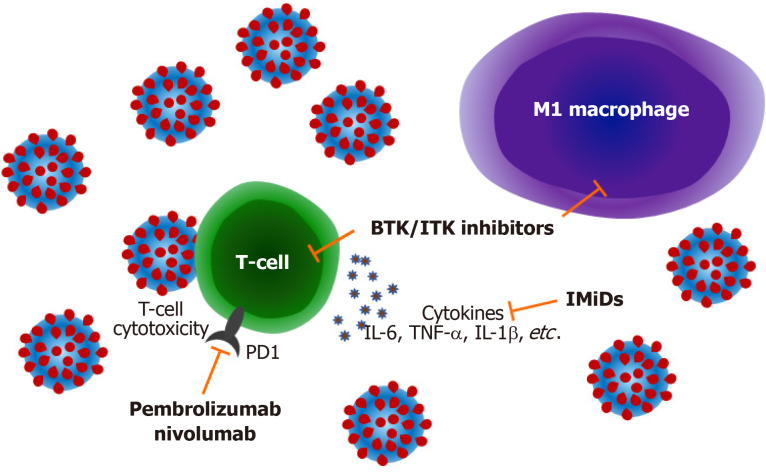
Figure 1.
Mechanisms by which lymphoma treatments may modulate coronavirus disease 2019 infection. Inhibition of Burton's tyrosine kinase and interleukin-2 inducible T-cell kinase modulates T-cell immune responses decreasing production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor α and interleukin-1b and also attenuating M1 macrophage polarization reducing pulmonary inflammation. Immune checkpoint blockade with drugs targeting programmed cell death 1 may improve antiviral cytotoxic T-cell responses. Immunomodulatory imide drugs can also block cytokine responses and improve T-cell function. BTK: Burton's tyrosine kinase; ITK: Interleukin-2 inducible T-cell kinase; PD1: Programmed cell death 1; IMiDs: Immunomodulatory imide drugs; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor α.