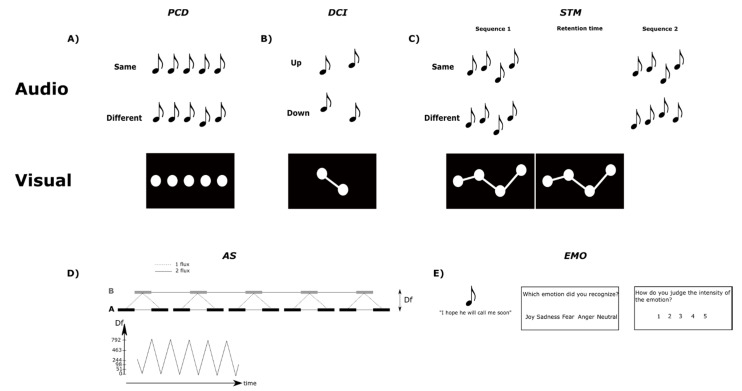
Figure 1.
Schematics of the five listening tests of the battery. (A) In the PCD test, the participants have to determine whether the fourth note is identical to or different from the others. (B) In the DCI test, the participants have to determine if the second note is higher (“up”) or lower (“down”) than the first note. (C) In the STM test, the participants have to compare two melodies (sequence 1 and sequence 2) and determine if they are identical or different. The bottom panels of (A–C) present a visual representation of the tones played simultaneously with the visual information. Note that the visual stimuli (disks) appear one at a time, simultaneously with a tone, and remain on the screen during the rest of the stimulation (PCD, DCI, STM), as well as during the retention delay before S2 (STM). (D) In the AS test, the participants hear a sequence of notes with ABA triplet repetitions (see the schematic on the top row of the panel), the frequency of A is fixed, and the frequency of B changes across time (see the corresponding frequency difference, Df). The sequence can be perceived as one stream or two streams. (E) In the EMO test, the participants hear a sentence with one emotion, and have to choose the correct emotion (Joy, Sadness, Anger, Fear, or Neutral) and then rate the corresponding intensity of this emotion (except for Neutral stimuli).