Figure 8.
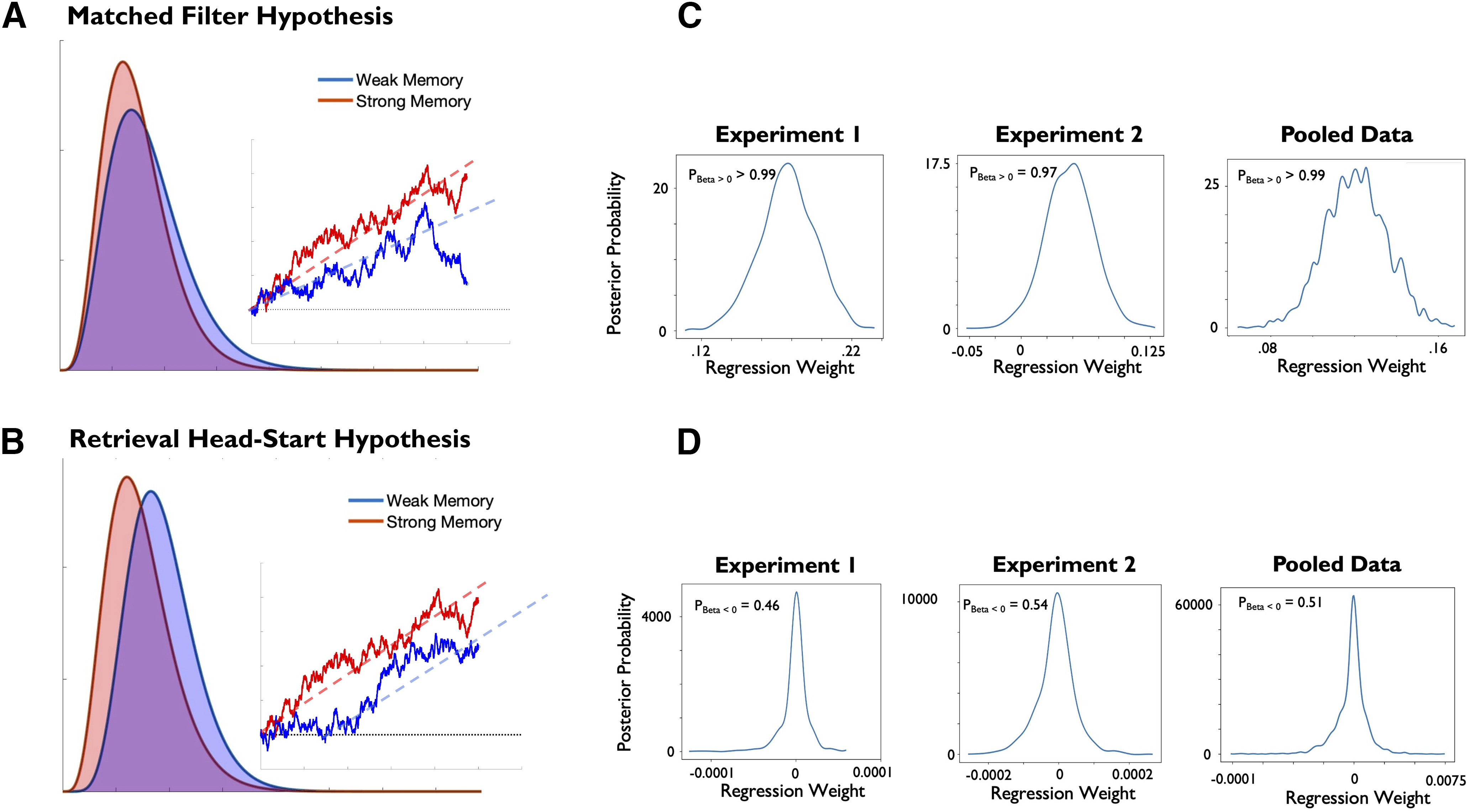
Drift diffusion modeling of task performance as a function of decoding strength of the active WM item. A, B, Illustration of the two hypotheses under investigation that predict that trial-wise variance in decoding of the cued item tracks either changes in drift rate (matched filter hypothesis) or non-decision time (retrieval head-start hypothesis). The plots display simulated RT distributions and exemplary single-trial diffusion patterns under the two accounts. C, D, Results of the DDM regression analysis that predicted trial-wise changes in drift rate (C) and non-decision time (D) based on trial-wise changes in decoding strength of the cued item. Plots display the posterior distribution of estimated regression weights, resulting from 5000 iterations from which the initial 1000 iterations were discarded as burn-in. The significance of effects was evaluated by quantifying the amount of the posterior probability mass that was in the predicted direction (positive for drift rate and negative for non-decision time; for details, see Materials and Methods, and Results). As indicated on the plots, decoding of the cued item reliably predicted changes in drift rate, but it was not associated with changes in non-decision time.
