Figure 4.
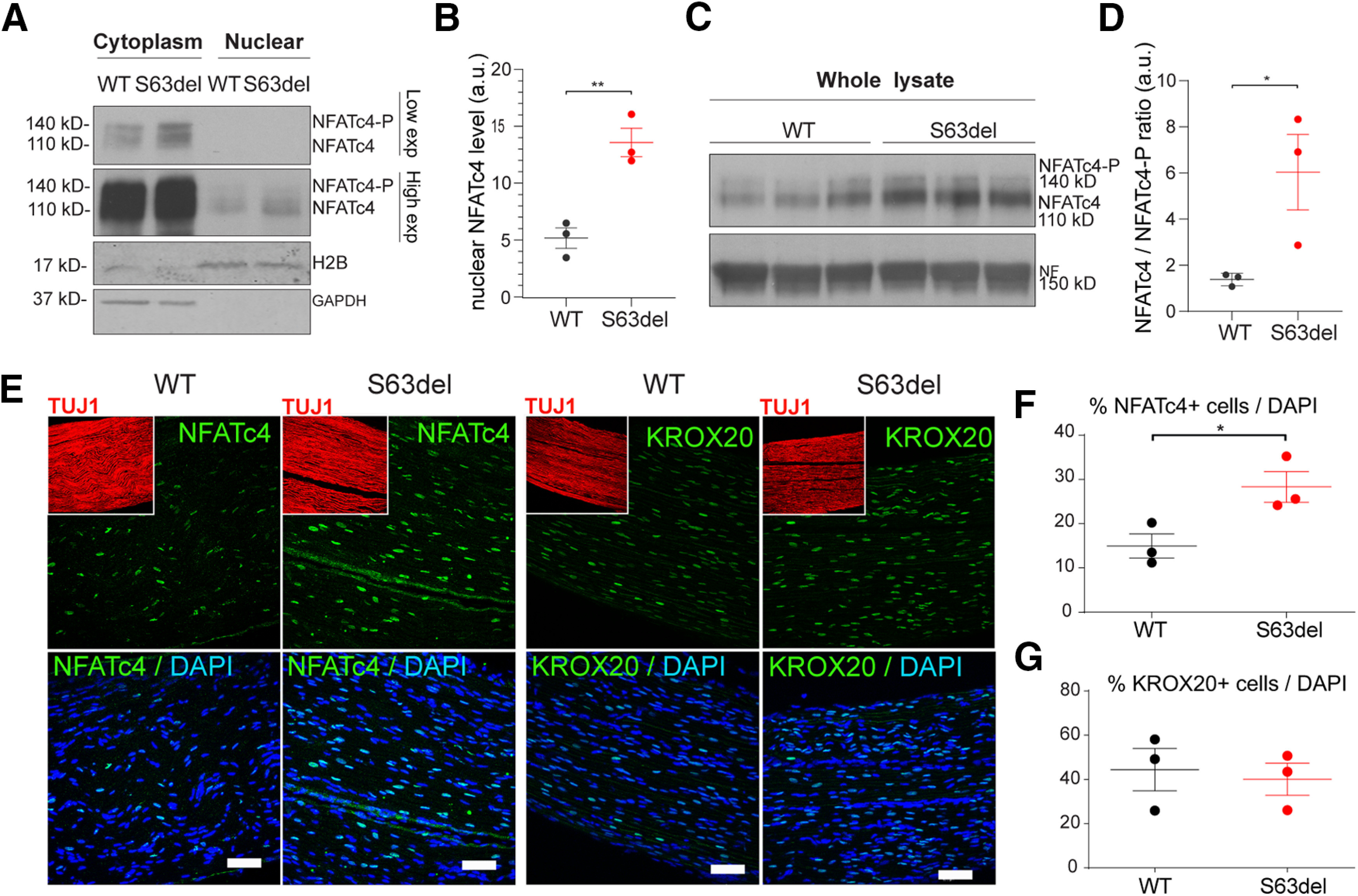
Nuclear NFATc4, but not Krox20, is increased in S63del nerves. A, Nuclear versus cytoplasmic enrichment of NFATc4 was obtained in WT and S63del sciatic nerves from P28 mice. Histone 2B (H2B) and GAPDH were used as marker of nuclear and cytoplasmic fraction, respectively. Nuclear NFATc4 appears with high exposure (High exp), whereas cytoplasmic NFATc4 is visible at lower exposure (Low exp). B, NFATc4 in the nuclear fraction was quantified in WT and S63del nerves, and H2B was used to normalize. Error bars indicate SEM. n = 3. **p < 0.01 (Student's t test). a.u., Arbitrary units. C, P28 sciatic nerves were homogenized from WT and S63del mice and incubated with NFATc4 antibody that recognizes phosphorylated (140 kDa) and nonphosphorylated NFATc4 (110 kDa). D, Quantified ratio of nonphosphorylated over phosphorylated NFATc4 protein level in C. Error bars indicate SEM. n = 3. *p < 0.5 (Student's t test). a.u., Arbitrary units. E, longitudinal cryosections of WT and S63del sciatic nerves from P28 mice were incubated with antibody against NFATc4 and KROX20 (green), Tuj1 for axons (red, insets), and DAPI for nuclei (blue). Scale bars, 50 μm. F, G, Graph represents the percentage (%) of nuclei positive for NFATc4 and KROX20 (E) staining as function of total DAPI-stained cells. Error bars indicate SEM. *p < 0.05 (Student's t test). n = 3.
