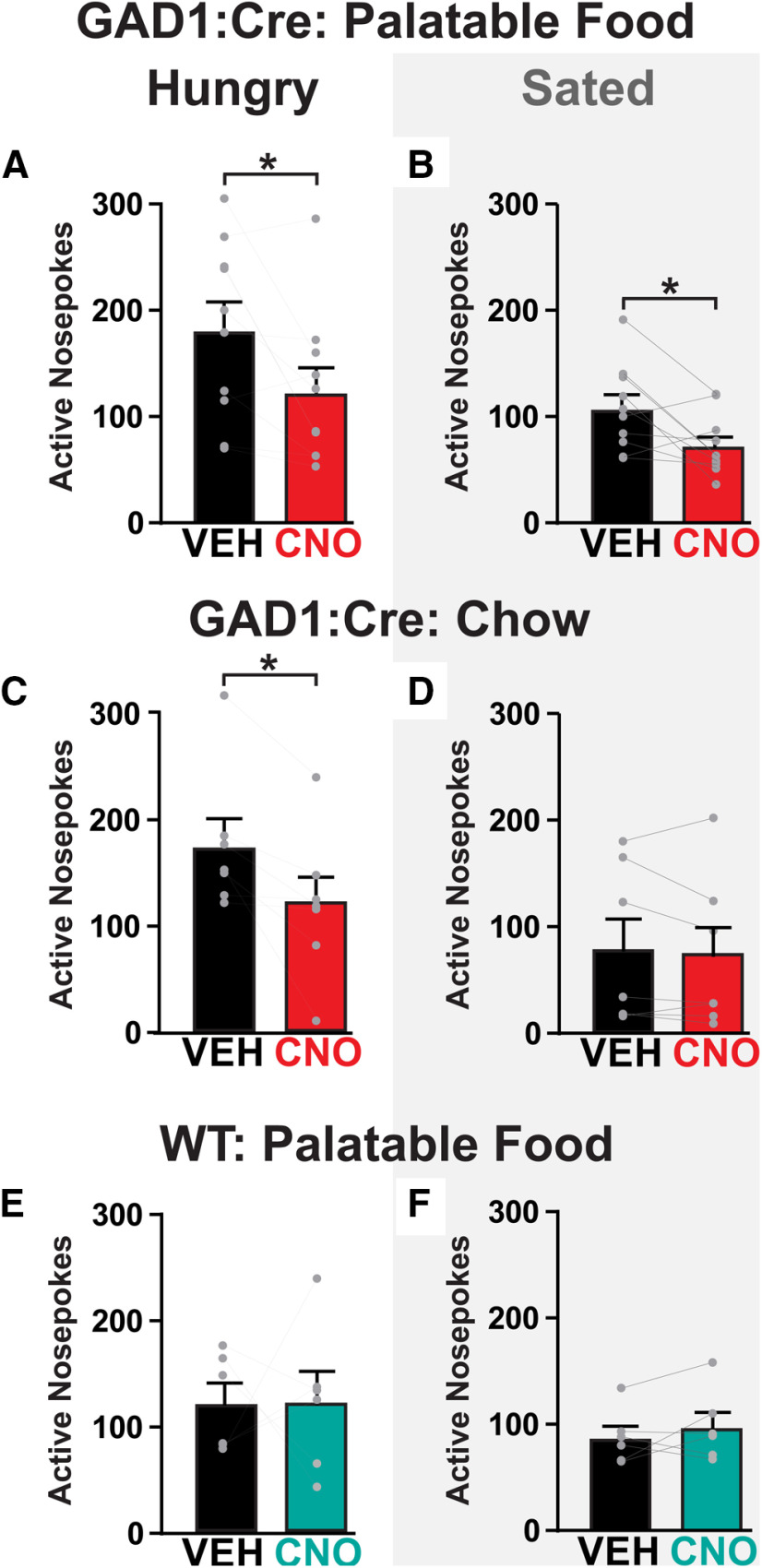
Figure 5.
Inhibiting VPGABA neurons reduces responding for palatable food and chow in hungry rats, but only reduces responding for palatable food (not chow) in sated rats. A, B, In GAD1:Cre rats, CNO (red bars) reduced FR1 active nose-pokes for palatable food in (A) hungry and (B) sated rats, relative to vehicle treatments (black bars). C, D, CNO in GAD1:Cre rats (red bars) reduced FR1 active nose-pokes for chow relative to vehicle (black bars) in (C) hungry, but not (D) sated rats. E, F, No effect of CNO on active nose-pokes in WT controls (teal bars) relative to vehicle treatment (black bars) under (E) hungry or (F) sated conditions. *p < 0.05 (paired-sample t test). Data are mean ± SEM. Dots represent individual rats.