Figure 6.
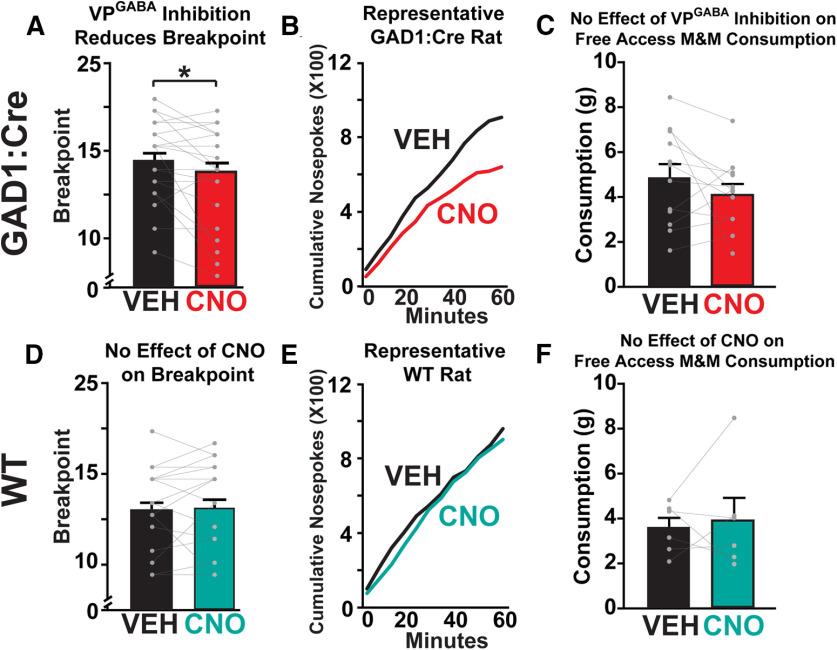
Inhibiting VPGABA neurons reduces progressive ratio motivation for palatable food, without impairing free access palatable chocolate intake. A, In GAD1:Cre rats, CNO (red bar) reduces break point relative to vehicle (black bar). B, Cumulative nose-pokes for a representative GAD1:Cre rat during vehicle (black line) and CNO (red line) progressive ratio tests are shown. C, CNO in GAD1:Cre rats (red bar) fails to alter 1 h free access M&M consumption, relative to vehicle test (black bar). D, In WT controls, CNO (teal bar) does not affect break point compared with vehicle day (black bar). E, Cumulative nose-pokes for representative WT rat during vehicle (black line) and CNO (teal line) progressive ratio tests are shown. F, CNO in WT rats (teal bar) fails to alter 1 h free access M&M consumption, relative to vehicle test (black bar). *p < 0.05 (paired-sample t test). Data are mean ± SEM. Dots represent individual rats.