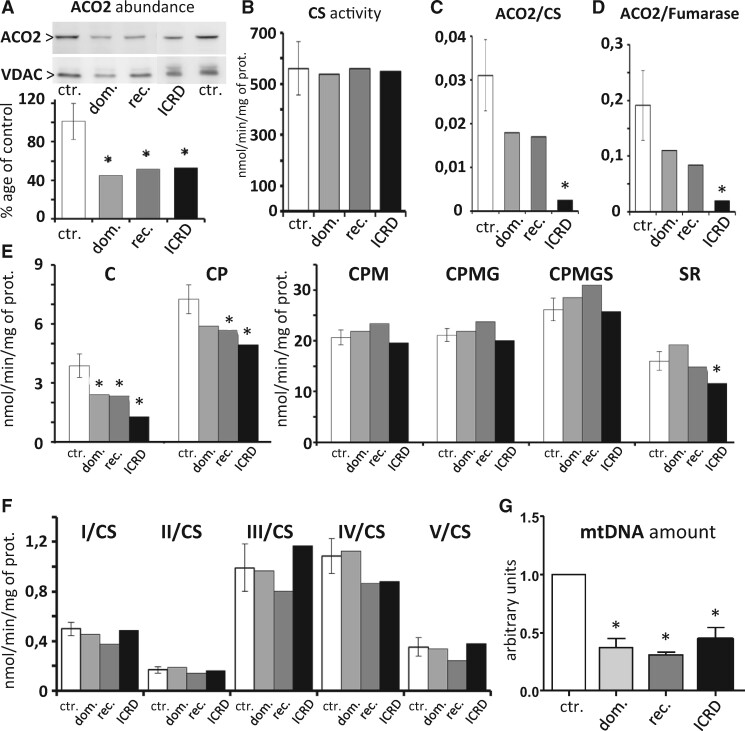
Figure 3.
Analysis of dominant and recessive ACO2 mutated fibroblasts, compared to an ACO2-related ICRD fibroblast cell line. All experiments were performed at least in two independent replicates for each control (ctr.) and dominant (dom.) and recessive (rec.) ACO2 fibroblasts, and compared to one ACO2-related ICRD fibroblast cell line (ICRD). Results are mean ± SD. Statistical analysis of results from all the following experiments was performed using the two-tailed paired t-test. (A) Western blots with antibodies against ACO2 and VDAC proteins. The quantification of the relative ratio shows a significant decrease of ACO2 protein in all patient fibroblasts (*P-value <0.05). (B) CS activity is not affected by ACO2 mutations. (C and D) Relative ACO2 activity normalized to the CS (C) and to the fumarase (D) activities shows a tendency to decrease in the dominant and recessive ACO2 fibroblasts, and a significant decrease in the ICRD fibroblasts (*P-value <0.05). (E) The assessment of fibroblast respiration (mitochondrial oxygen rates related to maximal phosphorylation condition in permeablized fibroblasts) by oxygraphy, using the Krebs cycle substrates, Citrate (C), pyruvate (P), malate (M), glutamate (G), succinate (S), followed by the inhibition of complex I by rotenone (R), show that the respiration related to the use of citrate is decreased in all ACO2 fibroblasts, partially increased by pyruvate, and fully restored by malate. Further stimulation by glutamate and succinate is limited, and only the ICRD fibroblasts are significantly more affected than the other fibroblasts by the Rotenone (*P-value <0.05). (F) Enzymatic activities from four independent experiments of the respiratory complexes (CI to CV) from the control and the ACO2 mutated fibroblast strains related to the CS enzymatic activity did not reveal a significant difference between control and mutated fibroblasts. (G) Mitochondrial DNA copy number in ACO2 mutated fibroblasts normalized to control fibroblasts reveals a significant decrease in the mitochondrial genome in all ACO2 cells (*P-value <0.05).