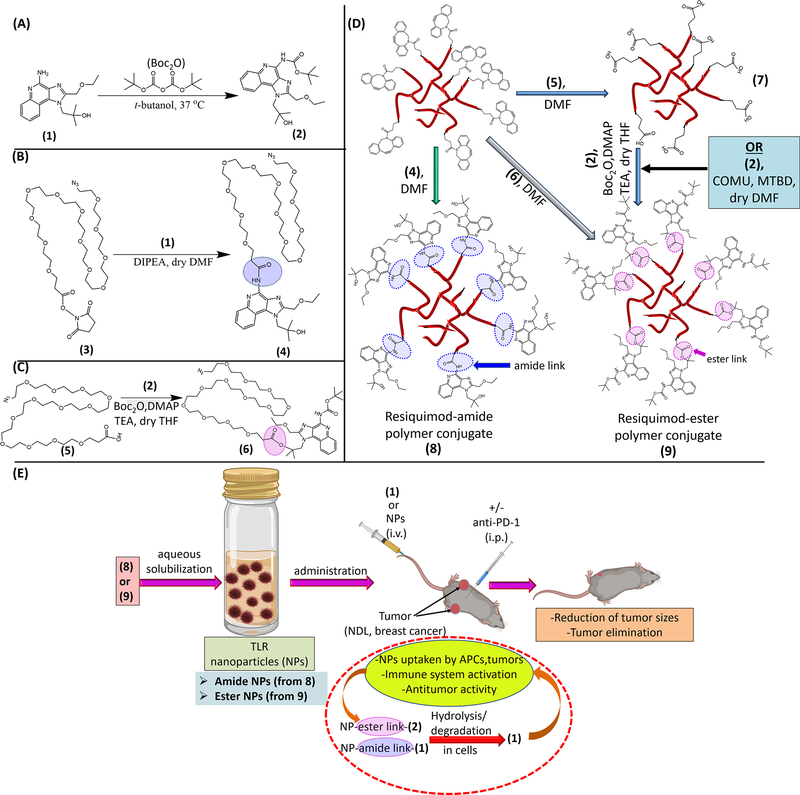
Scheme 1.
Schematic illustration of the materials and strategy employed for the design of the resiquimod prodrug NPs and their application in treatment of mice with established bilateral MBC tumors. Conversion of resiquimod (1) to Boc-protected resiquimod (2) (A).[55] Coupling of (1) to azido-PEG12-activated ester to afford azido-PEG12-resiquimod (3) with resiquimod linked to the polymer via an amide link (B). Synthesis of azido-PEG12-resiquimod with PEG linked to resiquimod via an ester link (6) (C). Preparation of amphiphilic hyperbranched polymer-resiquimod conjugates via strain promoted azide-alkyne reactions of an alkyne functionalized hyperbranched degradable polymer with either (4), (5) or (6) to obtain amphiphiles (7), carboxylic acid decorated amphiphile, and (8), [56–58] polymer-resiquimod amphiphile with resiquimod linked to the polymer via amide links, and formation of amphiphilic polymer-resiquimod conjugate with resiquimod linked to the polymer via ester links (9), (D). Formation of micellar NPs from the hyperbranched polymer-resiquimod conjugates and their application in treatment of mice with bilateral breast cancer tumors (E). NPs from (8) are referred to as amide NPs and those from (9) are termed ester NPs.