Figure 3.
Network-wide modulation of GoCs is correlated with behavioral engagement
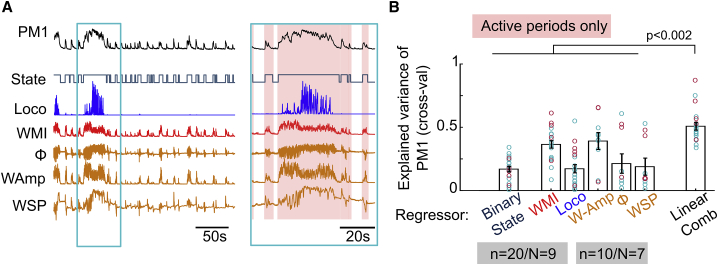
(A) Example of PM1, binary state and behavioral variables (whisker angle, Φ). Blue box shows the indicated region on expanded timescale, with active periods marked in light red.
(B) Cross-validated linear regression of PM1 to all behaviors. Explained variance (mean ± SEM): (state) 0.17 ± 0.03, (WMI) 0.36 ± 0.03, (Loco) 0.17 ± 0.03, (W-Amp) 0.39 ± 0.07, (Φ) 0.21 ± 0.08, and (WSP) 0.19 ± 0.07. Linear combination (Linear Comb, 0.49 ± 0.15) predicted PM1 significantly better than any of the individual behavioral variables (Mann-Whitney U test). Number of sessions (n) and animals (N) analyzed. Scatter represents individual sessions (Crus: cyan, Lob IV/V: magenta), bars and error bars indicate means ± SEMs across sessions.
See also Figure S4.