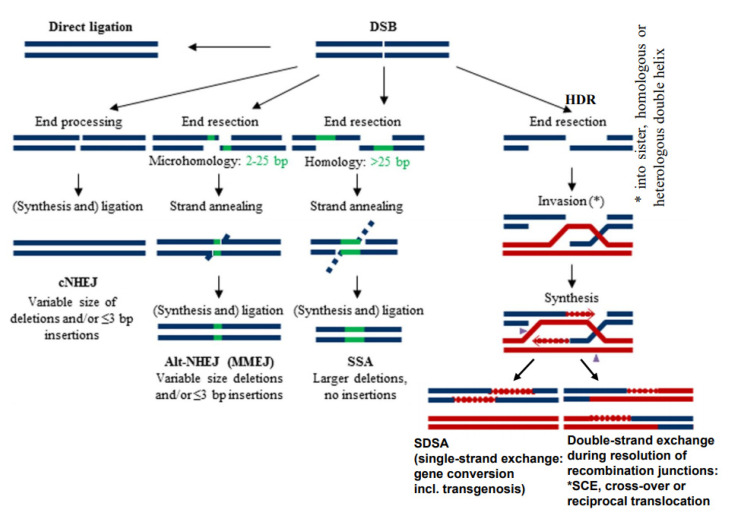
Figure 1.
Different modes of DSB repair (modified according to [11]). Various degrees of end resection, homology requirement and mutation outcome distinguish conservative non-homologous end-joining (cNHEJ), alternative or microhomology-dependent end-joining (altNHEJ/MMEJ) and single-strand annealing (SSA). All three differ from homology-dependent repair (HDR), where, after end resection, single-stranded overhangs invade an undamaged (partially) homologous double helix for synthesis over the gap region prior to re-annealing and ligation (synthesis-dependent strand annealing = SDSA). The latter results in gene conversion. In the same way, transgenic donor DNA can become integrated. Alternatively, the recombination structures (Holiday junction(s)) can be resolved in a way resulting in double-strand exchange between the damaged and the template molecule. Depending on the template molecule, double-strand exchange leads to sister chromatid exchange (SCE), meiotic cross-over or different types of rearrangements (see Figure 2).