Table 1. Statistical Parameters of the Catalysts Derived via Chemical and Solvothermal Reduction.
| synthesis | chemical
reduction |
solvothermal
reduction |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| parameter | Ni/C | Ni3Fe/C | Ni3Co/C | Ni3Cu/C | Ni/C | Ni3Fe/C | Ni3Co/C | Ni3Cu/C |
| L (nm)a | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 5.1 | 10.0 | 10.8 | 9.2 |
| Δd (nm)b | 3–19 | 3–33 | 3–61 | 3–26 | 4–12 | 10–18 | 7–43 | 9–25 |
| dav (nm)c | 11 ± 3 | 15 ± 3 | 23 ± 3 | 14 ± 3 | 8 ± 3 | 14 ± 3 | 21 ± 3 | 17 ± 3 |
| STEM (m2 gNi–1)d | 63 | 45 | 29 | 50 | 84 | 50 | 32 | 39 |
Crystallite size calculated from the Scherrer equation for the XRD diffraction peak for Ni(111): L = Kλ/β cos θ, where K ∼ 0.9 is a shape factor, λ is the wavelength for Cu Kα radiation, β is the full width at half-maximum (fwhm, in radians), and θ is the Bragg angle (in radians).
Δd: range of particle diameters based on the TEM image analysis.
dav:
average diameter calculated using the equation 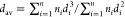 .
.
STEM: total surface area
calculated based on the TEM images using the
equation 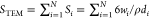 ;
; 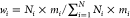 ; N: number of particles; Si: surface of all the particles
with the diameter di;
ρ = 8.9 × 106 g m–3 (density of Ni); wi: mass fraction of the particles with the diameter di; Ni: number of particles with the diameter di; mi: mass of one particle with the diameter di..
; N: number of particles; Si: surface of all the particles
with the diameter di;
ρ = 8.9 × 106 g m–3 (density of Ni); wi: mass fraction of the particles with the diameter di; Ni: number of particles with the diameter di; mi: mass of one particle with the diameter di..
