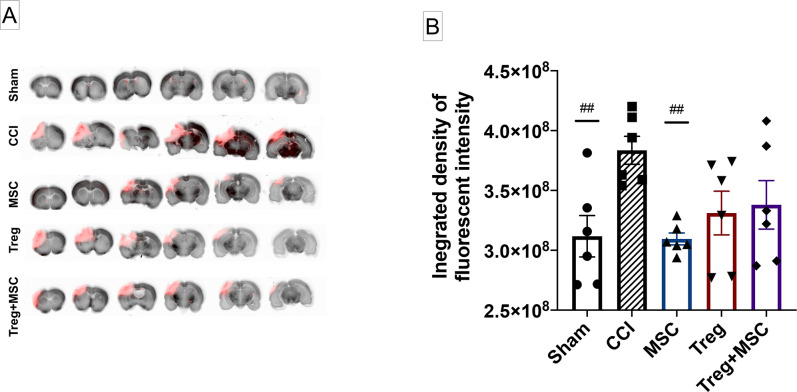
Fig 2. Assessment of blood brain barrier (BBB) permeability at 96 hours after CCI.
(A): Representative slices of the brain from forebrain to hindbrain, imaged using a LiCor Odyssey infrared scanner. Of note, the visual differences apparent between the groups do not directly correspond to quantitative changes in fluorescent intensity. (B): Quantitative assessment of BBB permeability, measured using the integrated density of fluorescence between intensities of 257–2827 which excludes background fluorescence and the focal cortical lesion, demonstrates that the BBB remains disrupted after CCI at 96 hours compared to sham. MSC monotherapy significantly reduced BBB permeability, while Treg monotherapy (p = 0.059) and Treg+MSC (p = 0.11) trended towards improvement. There were no significant differences between treatment groups. N = 6. Values of p ≤ 0.05 were considered significant. Statistical significance between sham/treatment and CCI is indicated with (#) for p ≤ 0.05, (##) for p ≤ 0.01, (###) for p ≤ 0.001. Statistical significance between treatment groups is indicated with (*) for p ≤ 0.05, (**) for p ≤ 0.01, (***) for p ≤ 0.001. CCI, controlled cortical impact.