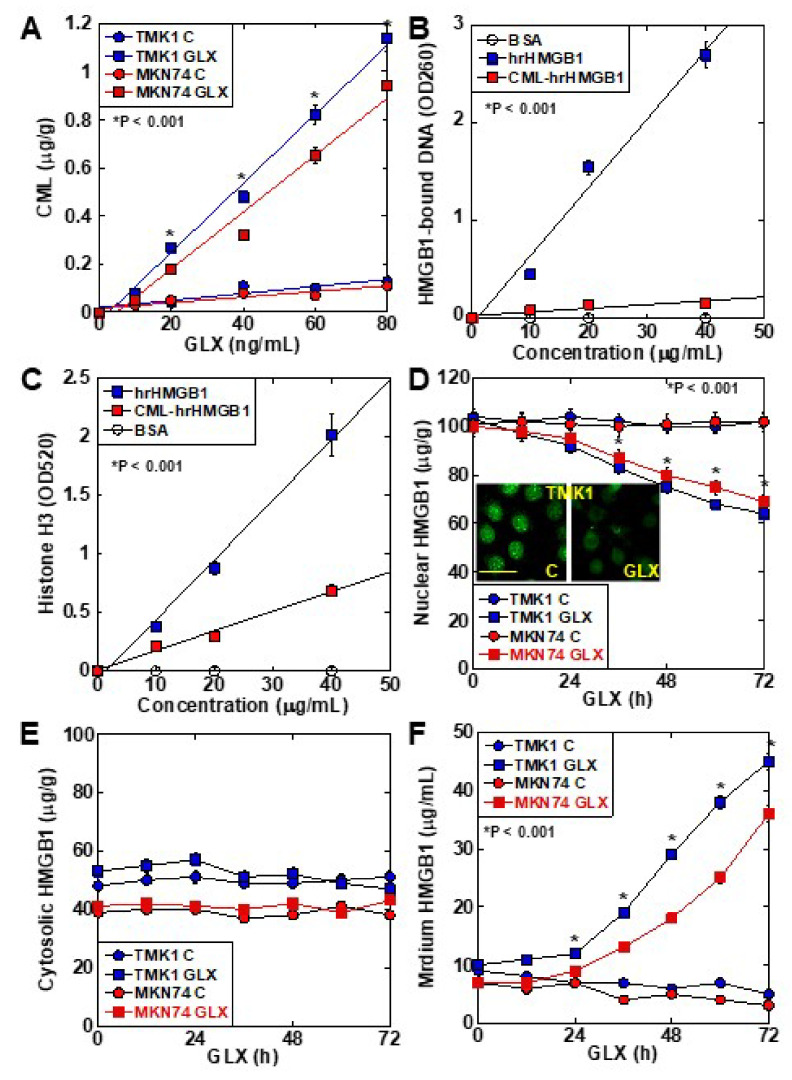
Figure 2.
Properties of CML formation in HMGB1 in TMK-1 gastric cancer cells. (A) CML formation in GLX-treated TMK-1 cells measured using ELISA. (B) Effect of glycation on DNA binding of HMGB1 in TMK-1 cells treated with HMGB1 or GLX (CML-HMGB1). DNA extracted from the nuclear protein immunoprecipitated by HMGB1 antibody was measured using a spectrophotometer (A260). (C) Effect of glycation on histone H3 binding to rhHMGB1 or CML-rhHMGB1. rhHMGB1 or GLX-treated rhHMGB1 (CML-HMGB1) were mixed with FITC-labeled histone H3. Histone H3 was measured using a fluorescence microplate reader (A520). (D–F) HMGB1 in the nuclear fraction (D), cytosol (E), and cultured medium (F) measured by ELISA in GLX-treated TMK-1 cells. The inset of panel D shows the fluorescent immunocytochemistry of HMGB1. Scale bar, 50 μm. Error bar and standard deviation calculated by ordinary analysis of variance from three independent experiments. CML, Nε-(Carboxymethyl)lysine; HMGB1, high-mobility group box-1; hr, human recombinant; GLX, glyoxal; OD, optical density; FITC, fluorescent isothiocyanate. * P < 0.001.