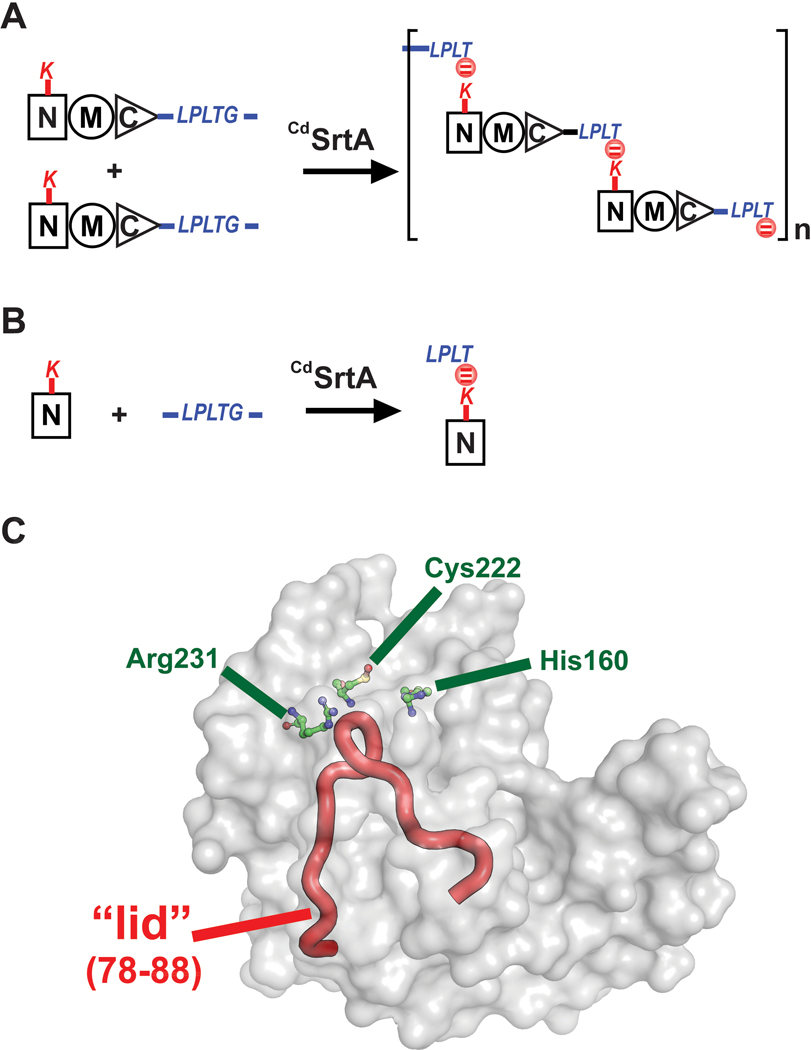
Figure 1.
The C. diphtheriae CdSrtA pilin sortase catalyzes lysine isopeptide bond formation. (A) Schematic showing the pilin polymerization reaction catalyzed by CdSrtA. The enzyme creates the SpaA pilus by polymerizing SpaA pilin proteins. In the reaction it recognizes lysine (K190) side chain nucleophile within the N-terminal domain of SpaA (NSpaA) and joins it the backbone threonine carbonyl carbon atom located in the C-terminal LPLTG sorting signal located within another SpaA protein. This reaction is repeated to construct the SpaA pilus that mediates bacterial adhesion. (B) Schematic of the reaction used to monitor lysine isopeptide bond formation. In this assay the CdSrtA enzyme ligates the isolated NSpaA domain to the peptide containing the LPLTG sorting signal (FELPLTGGSG). (C) The structure of CdSrtA showing H160, C222 and R231 active site residues. The “Lid” is highlighted in red (residues P77 to S89).