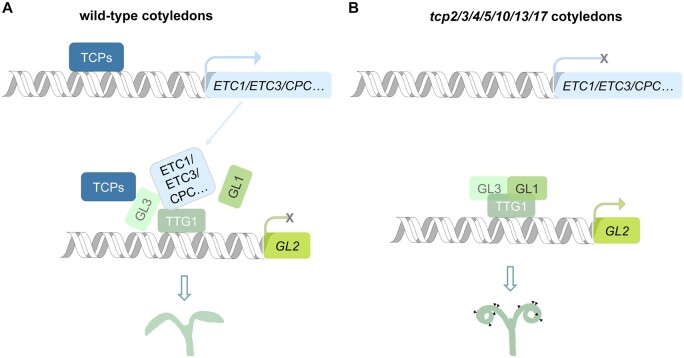
Figure 7.
The working model of TCP transcription factors controlling trichome formation on cotyledons. A, The schematic representation of the working model of TCPs in repression of trichome formation in wild-type cotyledons. TCPs directly increase the expression levels of R3 MYB genes. R3 MYB proteins and TCPs per se inhibit the transactivation activity of the MBW complex by directly interacting with the components of MBW to suppress the expression of the downstream gene GL2, causing glabrous cotyledons after seed germination. B, The schematic representation of the working model of trichome formation on cotyledons of the tcp2/3/4/510/13/17 mutant. Loss of functions of TCPs result in the inactivation of CPC, ETC1, ETC3, and TCL2. The lack of TCPs and these R3 MYB proteins cause the expressed GL3, GL1, and TTG1 to form an active MBW complex, promoting trichome formation.