Figure 4.
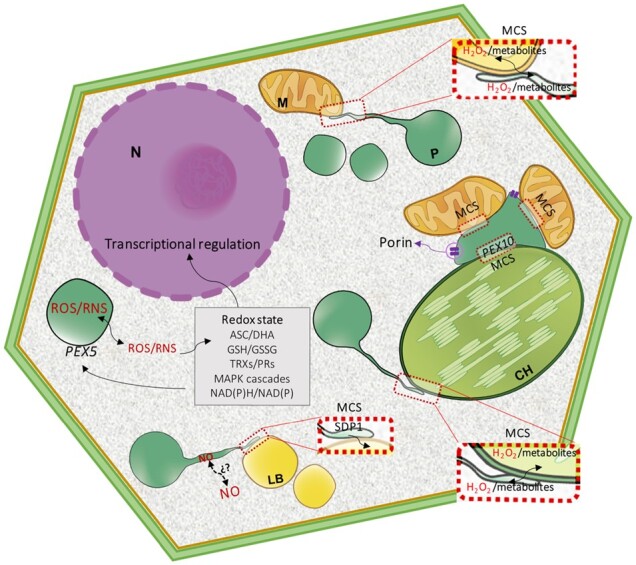
Redox-dependent interorganellar crosstalk. Peroxisomes (P) collaborate and communicate with other cellular organelles, mitochondria (M), and chloroplasts (CH) by exchanging molecules such as H2O2 and redox metabolites, as well as Ca2+ and proteins. These exchanges could take place through porins or MCSs. Peroxule formation contributes to ROS/RNS, metabolite, and protein exchanges such as the transfer of TAG lipase sugar-dependent 1 (SDP1) to lipid bodies (LB). ROS/RNS-dependent posttranslational modifications regulate peroxule formation, MCSs, interorganellar crosstalk, and signaling transduction. Peroxisomal ROS/RNS interferes with cytosolic redox state and signaling processes and vice versa; the cytosolic redox state regulates peroxisomal protein import by affecting the redox state of peroxin 5 (PEX5). The peroxisomal redox state can also regulate redox changes in the nucleus (N), chloroplasts, and mitochondria.
