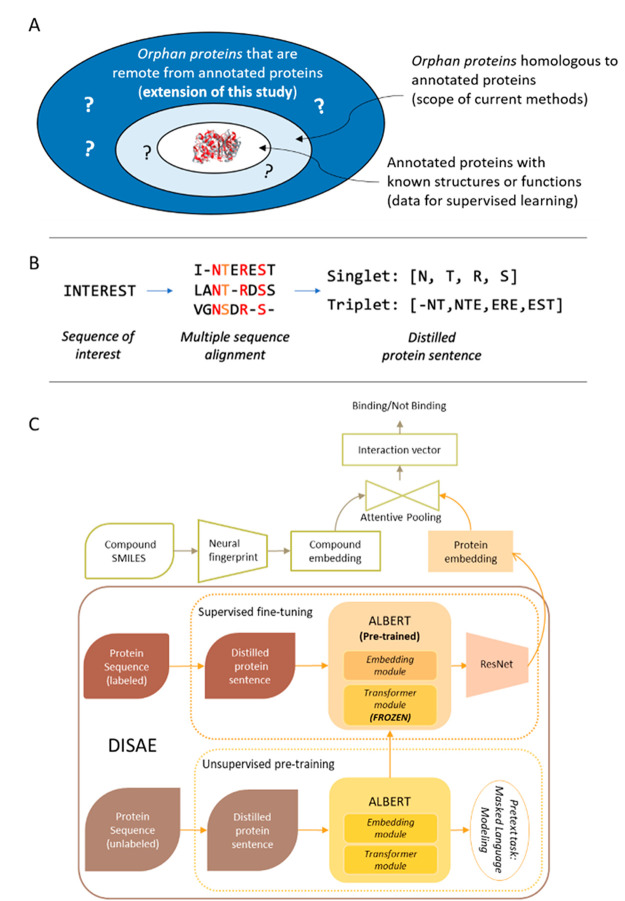
Figure 1.
(A) Comparison of the scope of this study with that of current works. In existing methods, only annotated proteins (labeled data) are used in the model training. They work well when an orphan protein is homologous to the annotated protein but mostly fail when the orphan protein is dissimilar from the annotated protein. By contrast, this study uses both annotated and orphan proteins in a self-supervised-learning-fine-tuning framework and thus extends the scope to genome-wide remote orphan proteins that are out of the reach of state-of-the-art. (B) Illustration of protein sequence representation from distilled sequence alignment. The high and medium conserved positions are marked as red and orange, respectively. (C) Architecture of deep learning model for the whole-genome CPI prediction.