Figure 1.
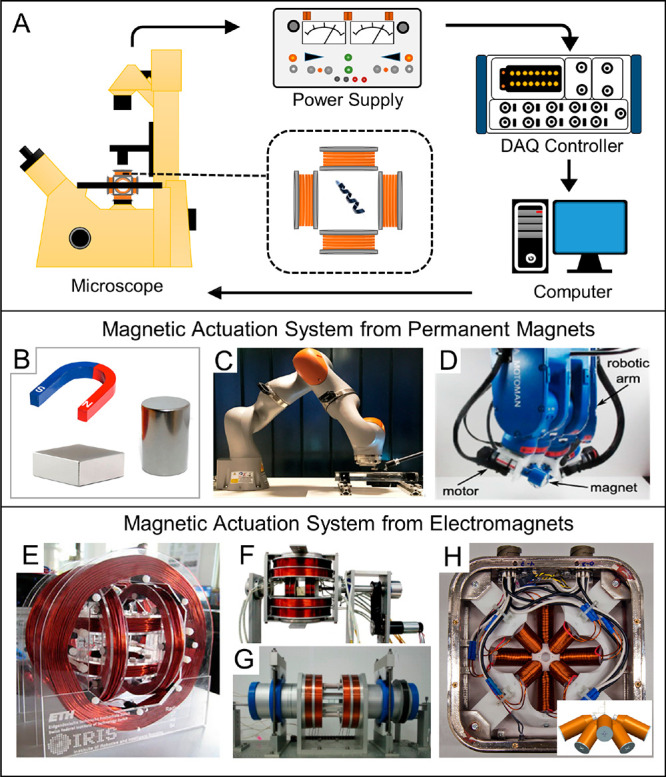
Experimental setup for magnetically driven micro/nanorobots and various magnetic actuation systems. (A) Diagram of the typical experimental workplace for actuating and visualizing MagRobots. (B) Magnetic actuation system consists of only a single permanent magnet. (C) Permanent magnet actuation system using cylindrical NdFeB permanent magnet fixed to its end-effector and a robotic arm. Reproduced with permission from ref (101). Copyright 2017 IEEE. (D) Rotating permanent magnet system consists of a magnet, a robotic arm, and a motor. Reproduced with permission from ref (102). Copyright 2013 IEEE. (E) Electromagnetic actuation system using triaxial circular Helmholtz coils. Reproduced with permission from ref (103). Copyright Springer Science + Business Media, LLC 2013. (F) Electromagnetic actuation system using a stationary Helmholtz–Maxwell coil and a rotational Helmholtz–Maxwell coil. Reproduced with permission from ref (104). Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. (G) Electromagnetic actuation system using multiply coils including a Helmholtz coil, Maxwell coil, uniform saddle coil, and gradient saddle coil. Reproduced with permission from ref (105). Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. (H) MiniMag electromagnetic system. Reproduced with permission from ref (106). Copyright 2014 Springer-Verlag GmbH Berlin Heidelberg.
