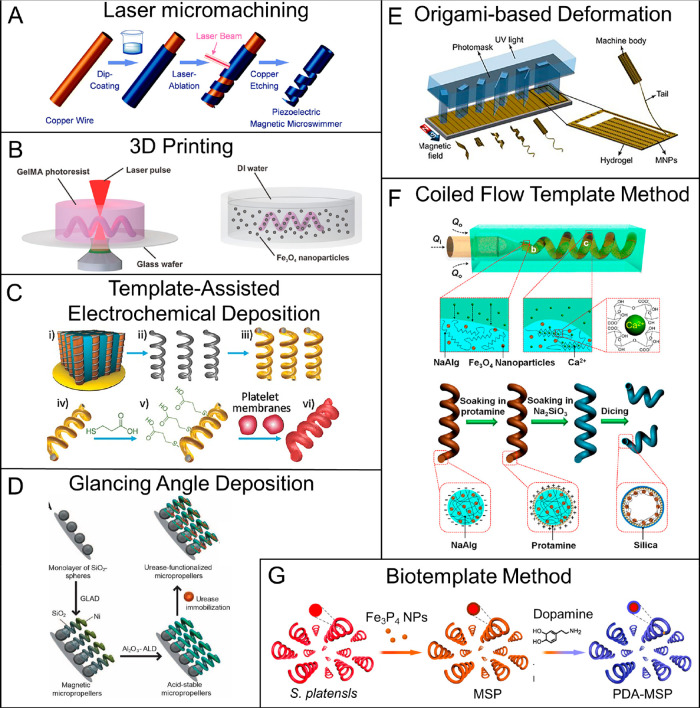
Figure 10.
Schematic illustrations of representative synthetic methods for helical MagRobots. (A) Fabrication process of piezoelectric magnetic microswimmers by laser ablation. Reproduced with permission from ref (217). Copyright 2019 The Royal Society of Chemistry. (B) Fabrication of biodegradable helical MagRobots using two-photon polymerization. Reproduced with permission from ref (238). Copyright 2018 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (C) Preparation process of platelet-membrane-cloaked MagRobots by TAED method including (i) Pd/Cu coelectrodeposition, (ii) etching of Cu and collection of helical structures, (iii) deposition of Ni and Au layers, (iv) collection of helical nanostructures, (v) surface modification, and (vi) fusion of platelet-membrane-derived vesicles to the modified surface. Reproduced with permission from ref (216). Copyright 2017 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (D) Preparation steps of acid-stable enzyme-functionalized MagRobots by GLAD. Reproduced with permission from ref (222). Copyright 2015 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. (E) Origami-inspired approach to prepare microswimmers by one-step photolithography. Reproduced with permission from ref (245). Copyright 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. (F) Fabrication of helical microrobots with hollow structures with the assistance of coiled flow template. Reproduced with permission from ref (223). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society. (G) Fabrication process of biohybrid microswimmers based on Spirulina platensis. Reproduced with permission from ref (226). Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society.