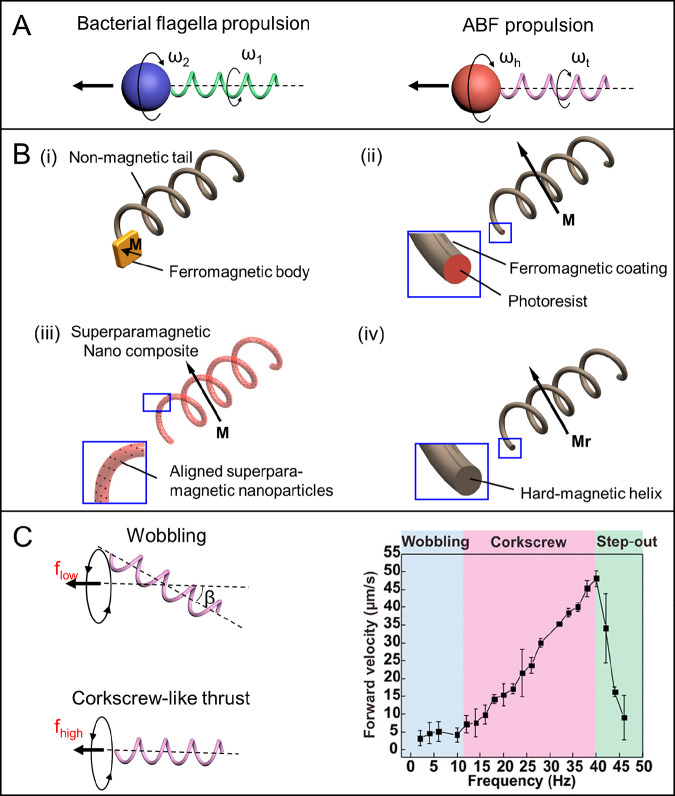
Figure 4.
Flagellar-based propulsion mechanisms. (A) Rotation of bacterial flagellum at frequency ω1 through rotary motor inside and a counter-rotation of the head at frequency ω2, while head and tail of ABF rotate in the same direction. (B) Typical types of magnetic ABFs. Reproduced with permission from ref (149). Copyright 2018 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (C) Field frequency-dependent ABF movement: ABF wobbles with a wobbling angle at low frequency; wobbling movement transforms into corkscrew-like swimming; then the wobbling decreases to zero at high rotational frequencies. Example of frequency-dependent propulsion of MOF-based helical swimmers. Reproduced with permission from ref (155). Copyright 2019 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, Weinheim.