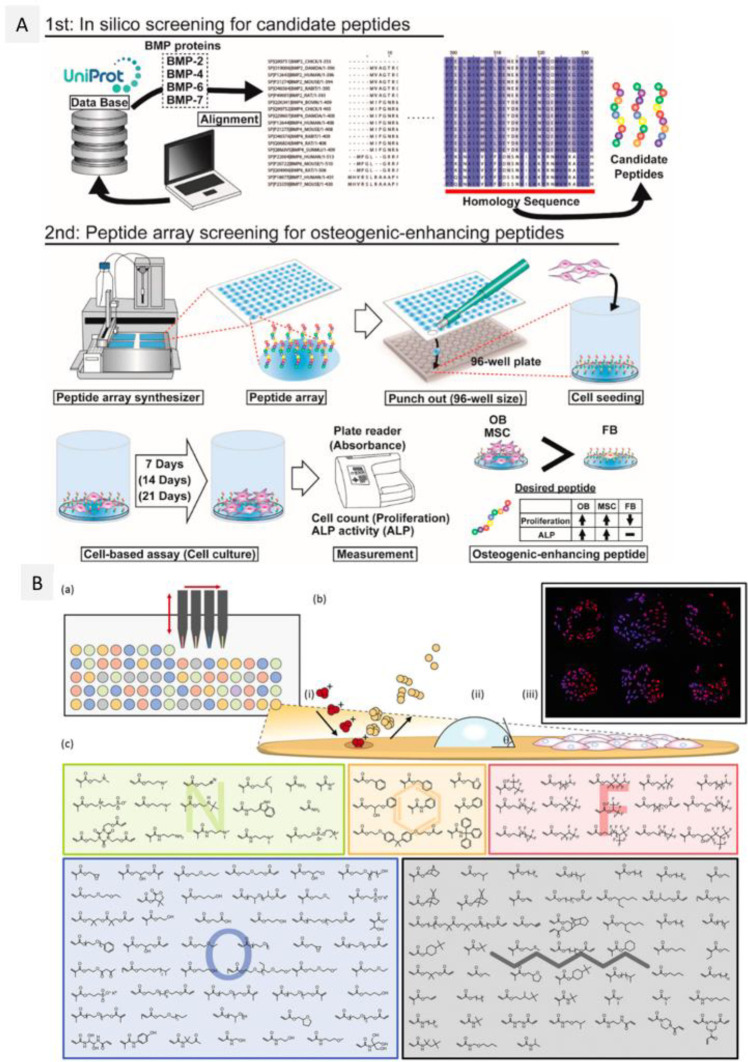
Figure 24.
Microarray strategies for 2D/surface printing of biomolecules and synthetic polymers. (A) Schematic of the strategy. Reprinted with permission from ref (501). Copyright 2016 MDPI. First, in silico screening of candidate peptides is performed, and candidate 9-mer peptides are selected from the homologous sequences. Second, the microarray is fabricated using a peptide array synthesizer on a cellulose membrane, which is cut and deposited in a 96-well plate. Cells are seeded, cultured, and assayed for cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation. (B) Polymer microarray. Reprinted with permission from ref (442). Copyright 2014 Royal Society of Chemistry. (a) Microarray fabrication using contact printing of monomer solution followed by UV polymerization, (b) high-throughput screening and characterization of polymer spots for (i) surface chemistry by ToF-SIMS, (ii) surface wettability using WCA, (iii) human stem cell adhesion and hit polymers with high cell attachment (inset); (c) structures of the 141 monomers used in the microarray, grouped by side-chain chemistry.