Figure 2.
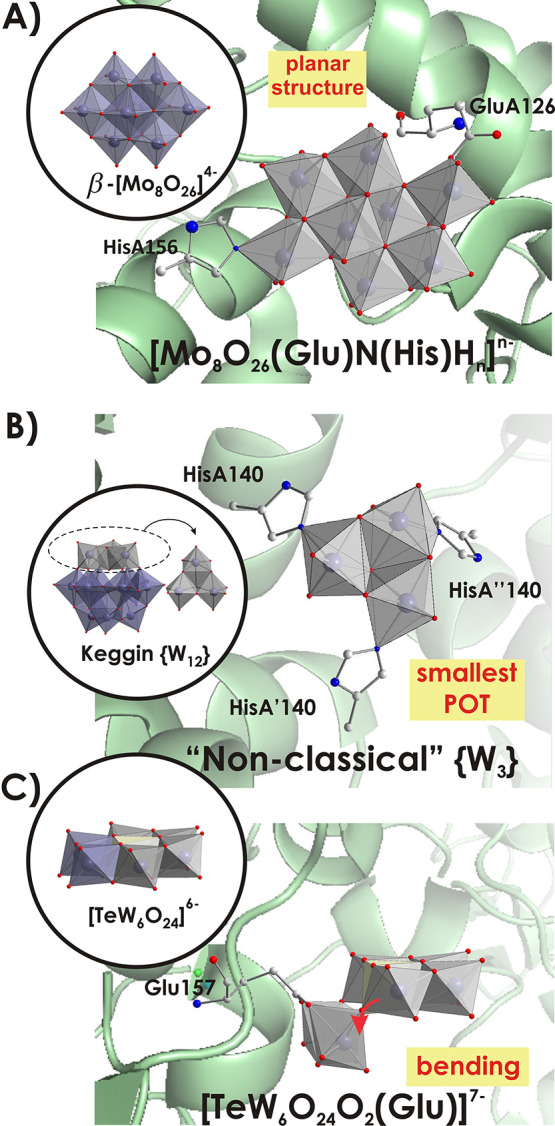
“Nonclassical” and classical POMos and POTs. (A) “Nonclassical” {Mo8} was found in the MoSto protein from A. vinelandii, and β-[MoVI8O26]4– could be crystallized from a Na2MoVIO4 solution acidified to a pH lower than 5.23c HisA156 and GluA126 are histidine and glutamate side chains. Color code: {MoO6}, gray or purple; C, gray; N, blue; O, red. (B) “Nonclassical” [WVI3O10HxN3](6–x)– {W3} was found in the WSto protein from A. vinelandii; metatungstate [H2WVI12O40]6– {W12} with its {W3} could be synthesized from a solution of Na2WVIO4 acidified to pH ∼ 5.23d HisA140, HisA′140, and HisA″140 are histidine side chains from three α subunits. Color code: {WO6}, gray or purple; O, red. (C) Covalent binding of TEW24 to the polyphenol oxidase cgAUS1.25a The carboxylic O atoms of glutamic acid (Glu157) bind covalently to two W atoms of TEW, accompanied by a rearrangement within the Anderson–Evans structure resulting in a bent structure term.24 For comparison, the normal Anderson–Evans structure is depicted as polyhedra in the inset to the left in a matching orientation. Color code: {WO6}, gray or purple, where the gray color indicates “nonclassical” fragments in “classical” structures; {TeO6}, pale yellow; C, gray; N, blue; O, red.
