Figure 2.
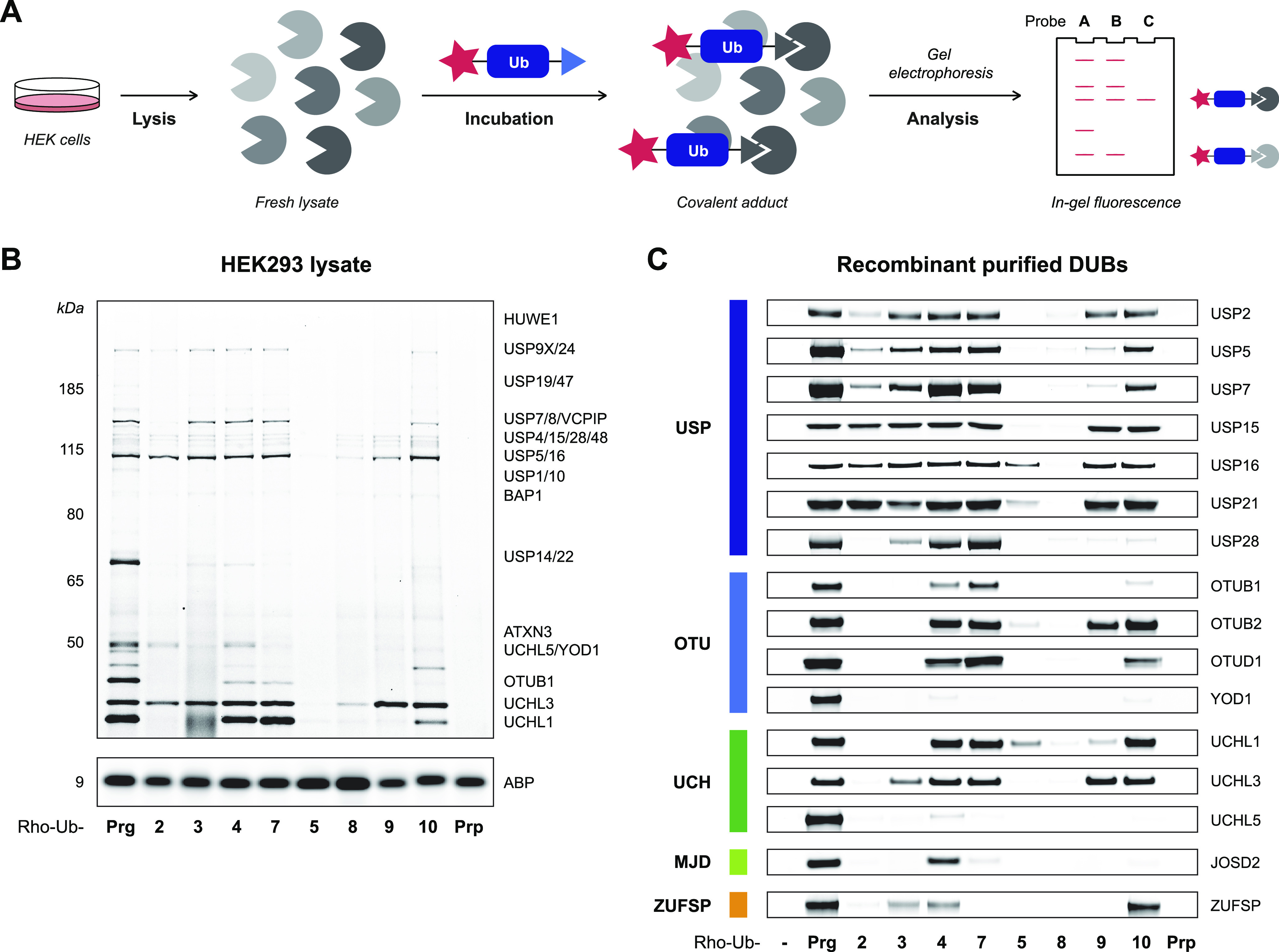
Incubation of whole lysate and purified recombinant DUBs with Rho-Ub-alkyne ABPs. (A) Incubation of whole lysate with Rho-Ub-ABPs to identify covalent ABP-DUB adducts. (B) Fluorescence scan of HEK293 lysate incubated with Rho-Ub-ABP (10 μM) reveals that acceptance of alkyne substituents is DUB-specific. Assignment of labeled DUBs based on proteomic analysis by Altun et al.14 Darker bands correlate with more covalent ABP–enzyme adduct, but the maximum intensity depends on total protein expression. Fluorescence scans of HEK293 or EL4 lysate incubated with 1 or 10 μM Rho-Ub-ABP are shown in Figure S2. Full gel scans and loading controls are provided in Figure S6. (C) Fluorescence scan of recombinant purified cysteine DUBs incubated with Rho-Ub-ABP (10 μM). Fluorescence intensity was normalized to Rho-Ub-Prg adduct. DUB conversion to covalent adduct (visualized with Coomassie protein stain) is shown in Figure S3. Constructs and source of recombinant purified cysteine DUBs are specified in Table S2. Full gel scans and loading controls are provided in Figures S9 and S10.
