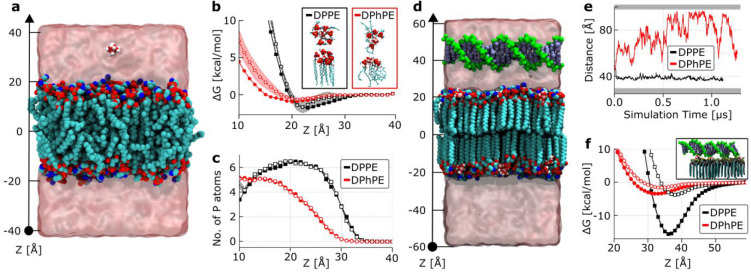
Figure 2.
MD simulation of Mg2+-modulated binding of DNA to fluid and gel-phase membranes. (a) Typical system used for the replica-exchange umbrella sampling simulations of Mg2+ affinity to a lipid membrane. Non-hydrogen atoms of the lipid (DPhPE) membrane are shown as blue (N), tan (P), red (O), and cyan (C) spheres. One magnesium ion and its first solvation shell, Mg[H2O]62+, are shown explicitly by using red and white spheres; the semitransparent surface illustrates the volume occupied by the MgCl2 solution. (b) Free energy of Mg[H2O]62+ versus distance to the midplane of the lipid membrane. The z-axis is defined in panel (a). Insets illustrate a representative coordination of the magnesium ions by lipid headgroups at the minimum of the respective free energy curves. Open and filled symbols indicate data for single ion and 100 mM MgCl2 buffer conditions, respectively. (c) Number of phosphorus atoms of the lipid headgroups within 1 nm of a Mg[H2O]62+ ion versus its distance from the membrane midplane. (d) Typical system used in simulations probing dsDNA affinity to a lipid membrane; DPPE membrane is shown. The backbone and bases of the 21-base pair DNA fragment are shown in green and blue, respectively. The DNA’s backbone is connected to itself across the periodic boundary of the system. (e) Distance between the center of the DNA and the midplane of the lipid membrane during free-equilibration simulations. The shaded region at the bottom of the plot shows the approximate location of the lipid membrane with which the DNA is interacting, while the top shaded region marks its periodic image along the z-axis. (f) Free energy of the 21 bp DNA fragment versus its distance to the membrane midplane. The inset image illustrates a representative instantaneous configuration of Mg[H2O]62+ ions near DNA at its free energy minimum. Open and filled symbols indicate data for 4 and 20 mM concentration of MgCl2, respectively.