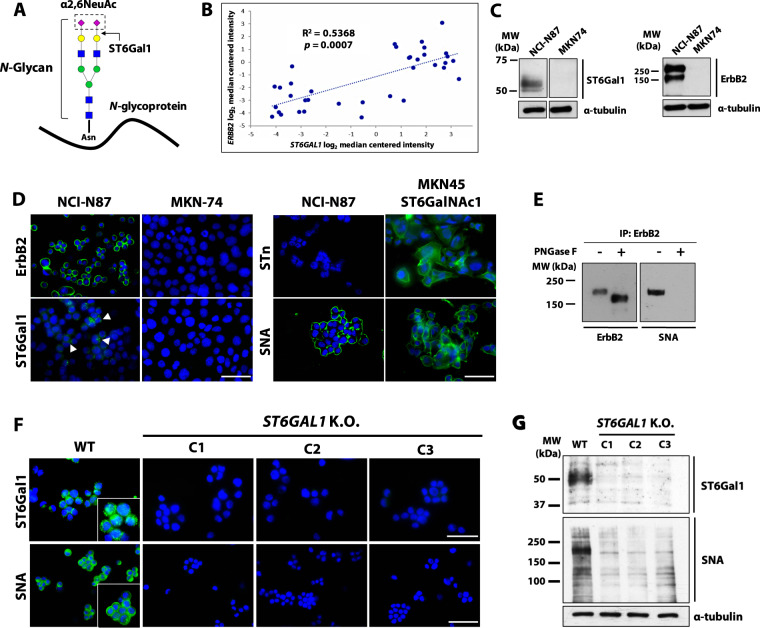
Fig. 2. ST6GAL1 K.O. abrogates the cell surface expression of α2,6-linked sialic acid in ErbB2-positive gastric cancer cells.
A Schematic representation of terminal α2,6-sialylation (α2,6NeuAc) of N-glycosylated proteins via ST6Gal1; B Positive Spearman’s rank correlation between the ERBB2 and ST6GAL1 transcript expression in gastric cancer (GC) patients from the DErrico dataset available at the OncomineTM database; C Western blot analysis of ErbB2 and ST6Gal1 expression in intestinal-type GC cell lines; D Immunofluorescence detection of ErbB2, ST6Gal1, and total (Sambucus nigra agglutinin (SNA)) and O-linked (sialyl Tn (STn)) α2,6-linked sialic acid (α2,6NeuAc) in intestinal-type GC cell lines; DAPI nuclear staining is shown in blue; The scale bar corresponds to 60 μm; E Western blot analysis of ErbB2 and α2,6NeuAc following receptor immunoprecipitation from NCI-N87 whole cell lysates and Peptide N-Glycosidase F (PNGase F) digestion; F Immunofluorescence detection of ST6Gal1 and its glycan product (α2,6NeuAc) in NCI-N87 WT and ST6GAL1 K.O. cells; DAPI nuclear staining is shown in blue; The scale bar corresponds to 60 and 40 μm, in the ST6Gal1 and SNA panels, respectively; G Western blot analysis of ST6Gal1 and α2,6NeuAc (SNA) expression in NCI-N87 WT and ST6GAL1 K.O. cells; C1 clone 1, C2 clone 2, C3 clone 3.