Figure 2. Somatic mutations in 68 GCAs.
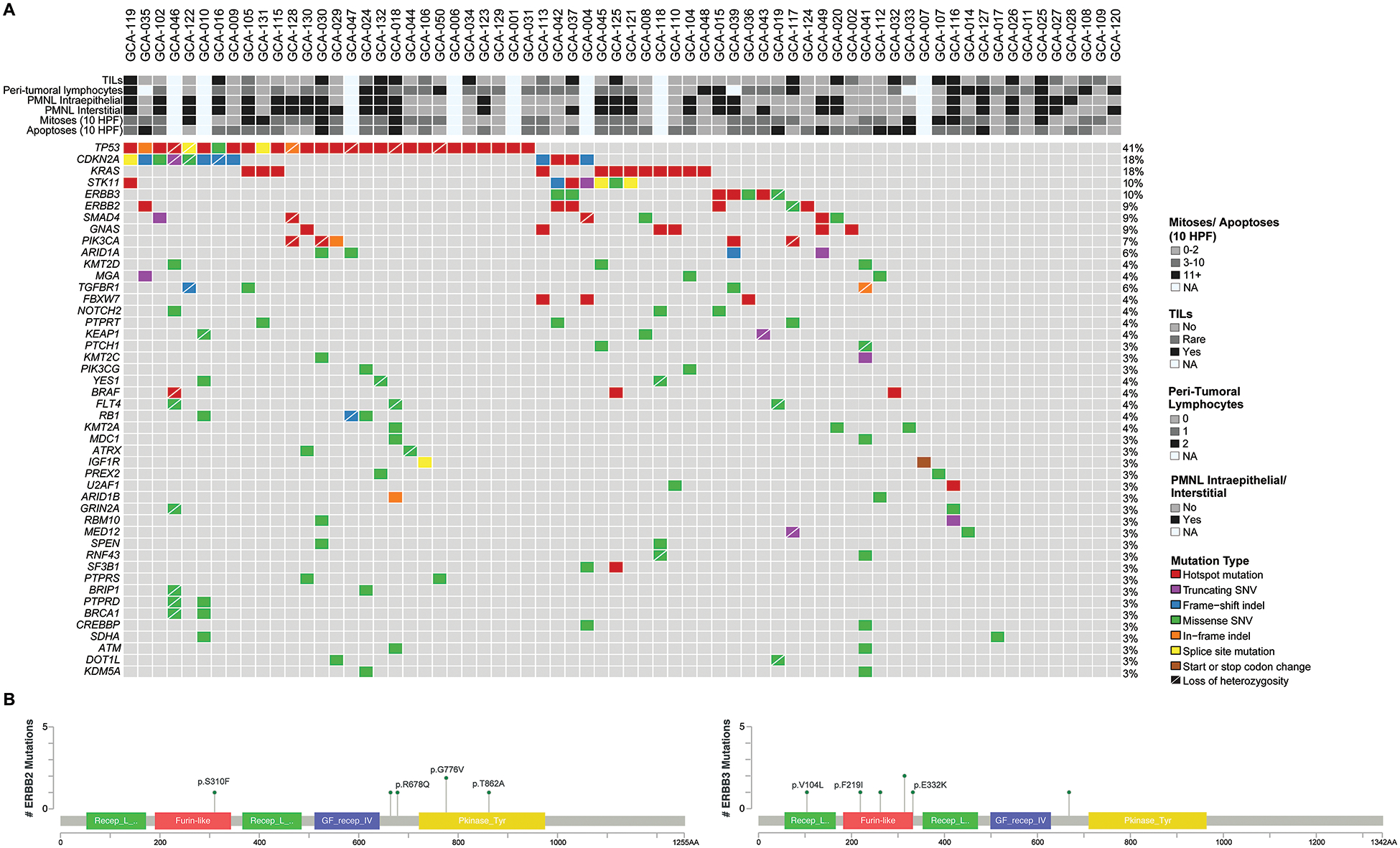
A) Recurrent non-synonymous somatic mutations affecting 410–468 cancer-related genes in 68 GCAs are shown, color-coded in the legend. The most common mutations involved TP53 (41%) and CDKN2A (18%). Clinicopathologic features are shown in the phenobar. TILs, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes; PMNL, polymorphonuclear leukocytes; Indel, small insertion and deletion; SNV, single nucleotide variant. B) Schematic representation of the protein domains of ERBB2 (left) and ERBB3 (right) and the somatic mutations identified in GCAs. Mutational frequency is represented by the height of each lollipop (y-axis). Hotspot mutations are annotated showing the amino acid changes.
Note: In addition, three other cases that were not diagnosed as GCA were also sequenced. Two were gastric-type adenocarcinomas in situ (gAIS), one of which harbored a nonsense mutation in STK11 and missense mutations in ERBB3 and TP53, while a CDKN2A nonsense mutation was identified in the other case. One was a case of lobular endocervical glandular hyperplasia, in which a frameshift mutation in CDKN2A and a hotspot mutation in GNAS were identified.
