Figure 2. Morbidities of Infants born Extremely Preterm in the Japanese Neonatal Research Network.
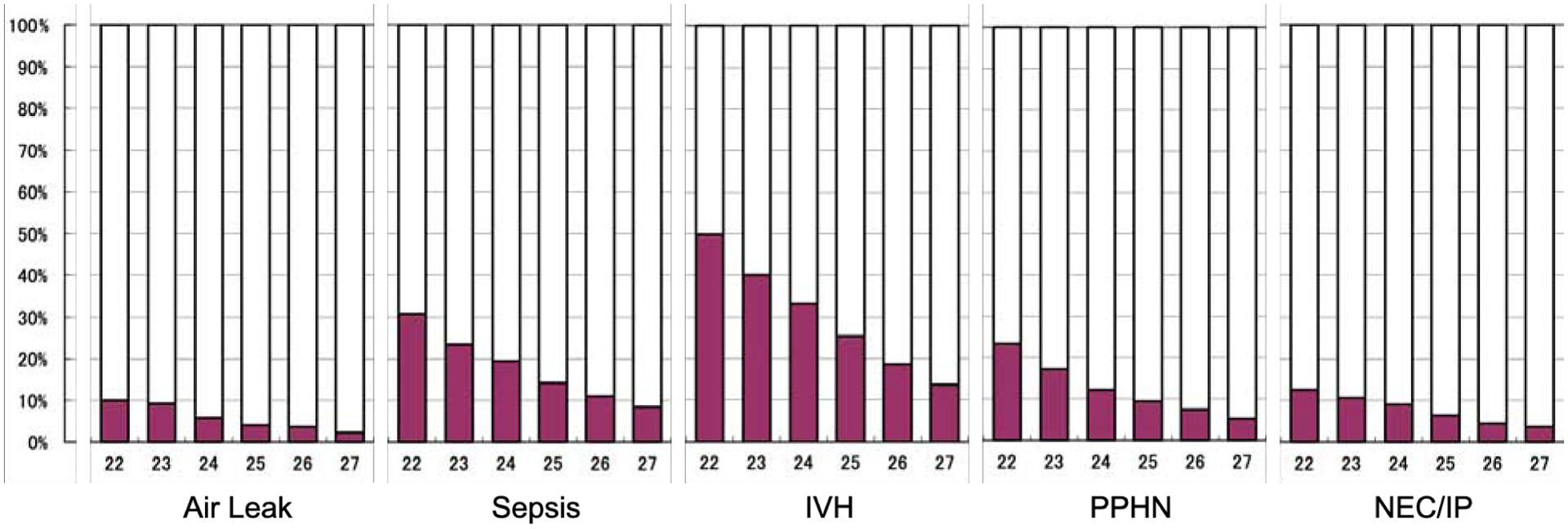
In-hospital morbidities for live born infants with extreme prematurity in the Japanese Neonatal Research Network 2003–2017 by gestational age at birth.64 Air leak includes pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum. Sepsis was defined as a positive blood culture at any time after birth. Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) includes all grades. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) was defined as a right-to-left shunt at the foramen ovale and/or ductus arteriosus, without cardiac anatomical abnormality, diagnosed by echocardiography. Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) was defined as Bell stage II or greater; intestinal perforation (IP) was diagnosed if free air in the abdomen for a reason besides NEC. The denominator includes all live births (n=943 at 22 weeks; n=2712 at 23 weeks; n=3764 at 24 weeks; n=4366 at 25 weeks; n=5278 at 26 weeks; n=6161 at 27 weeks).
