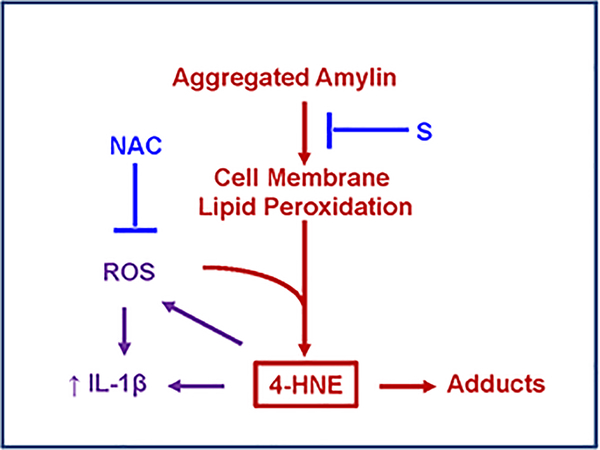
Figure 2. Proposed mechanism for amylin-mediated lipid peroxidation cell membrane injury and activation of IL-1β pro-inflammatory signaling pathway.
(adapted from Ref. 15). Amylin inclusions in cellular membranes generate reactive aldehydes such as 4-hydroxnonenal (4-HNE) that perturb intracellular homeostasis, leading to increased synthesis of IL-1β. Blocking either cellular amylin uptake (by a surfactant cell membrane stabilizer; S), or the lipid peroxidation chain reaction (by N-acetyl cysteine; NAC), demonstrate that peroxidative membrane injury is upstream of IL-1β increased synthesis.