Figure 5. Cardiomyocyte-specific Txnip C247S hearts have increased anti-oxidative activities following myocardium infarction.
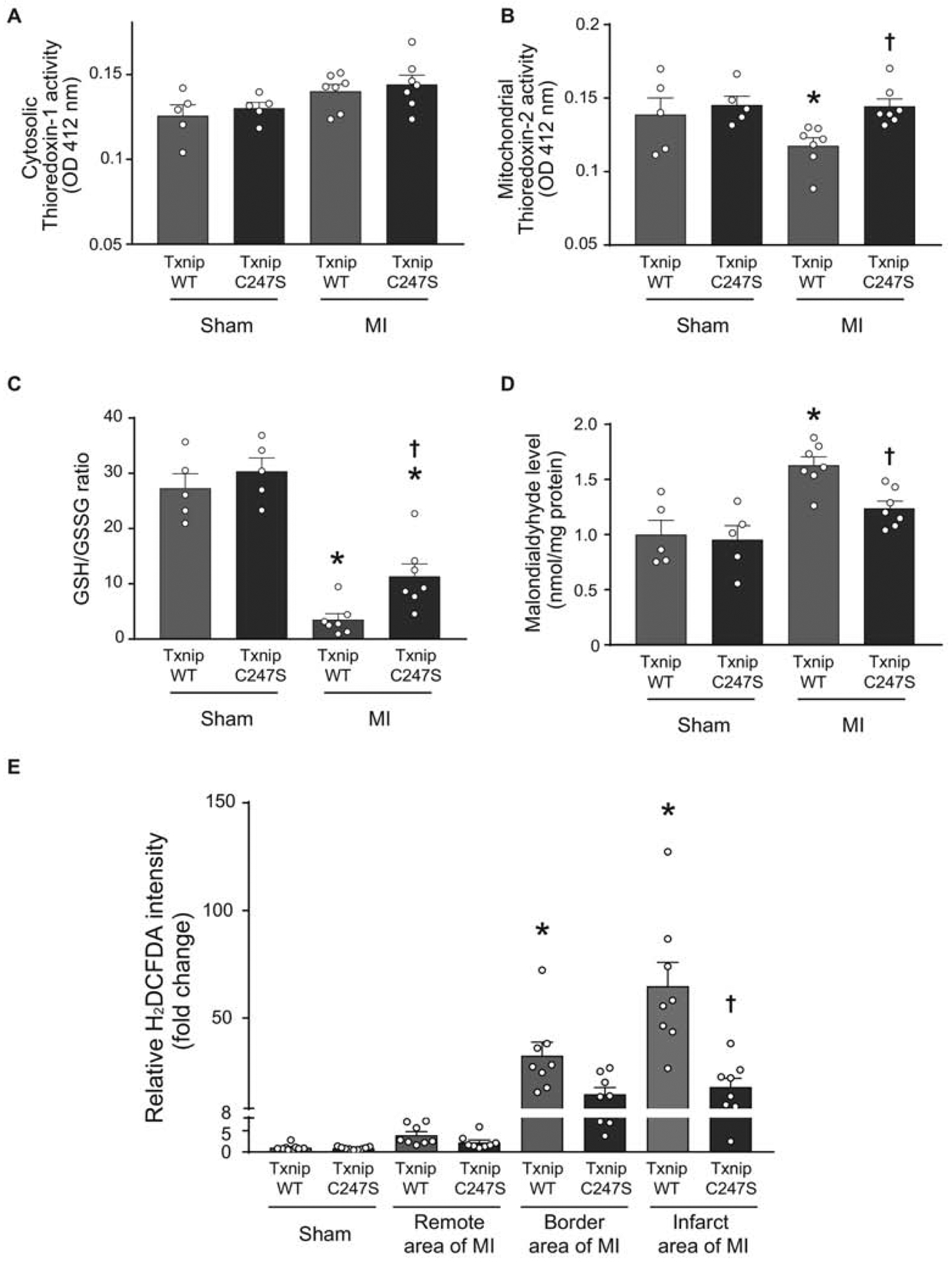
A and B. Thioredoxin’s reducing activities were measured in cytosolic (A) and mitochondria (B)-enriched fractions from the heart tissues of mice that underwent experimental MI or sham surgeries. *P<0.05 vs. Sham, †P<0.05 vs. WT MI. C and D. Tissue levels of GSH/GSSG ratio (C) and malondialdehyde (D) were analyzed in the mouse heart as markers of oxidative stress. *P<0.01 vs. Sham, †P<0.05 vs. WT MI. E. Frozen sections of the mouse heart were stained with a fluorogenic dye H2DCFDA that measures ROS activity within the myocardium. The fluorescence intensity was expressed in the remote, border, or infarct area as a relative change over the Sham group. *P<0.01 vs. Sham and remote area, †P<0.01 vs. WT infarct area.
