Figure 7. Mechanisms by which Txnip C247S achieves cardioprotection.
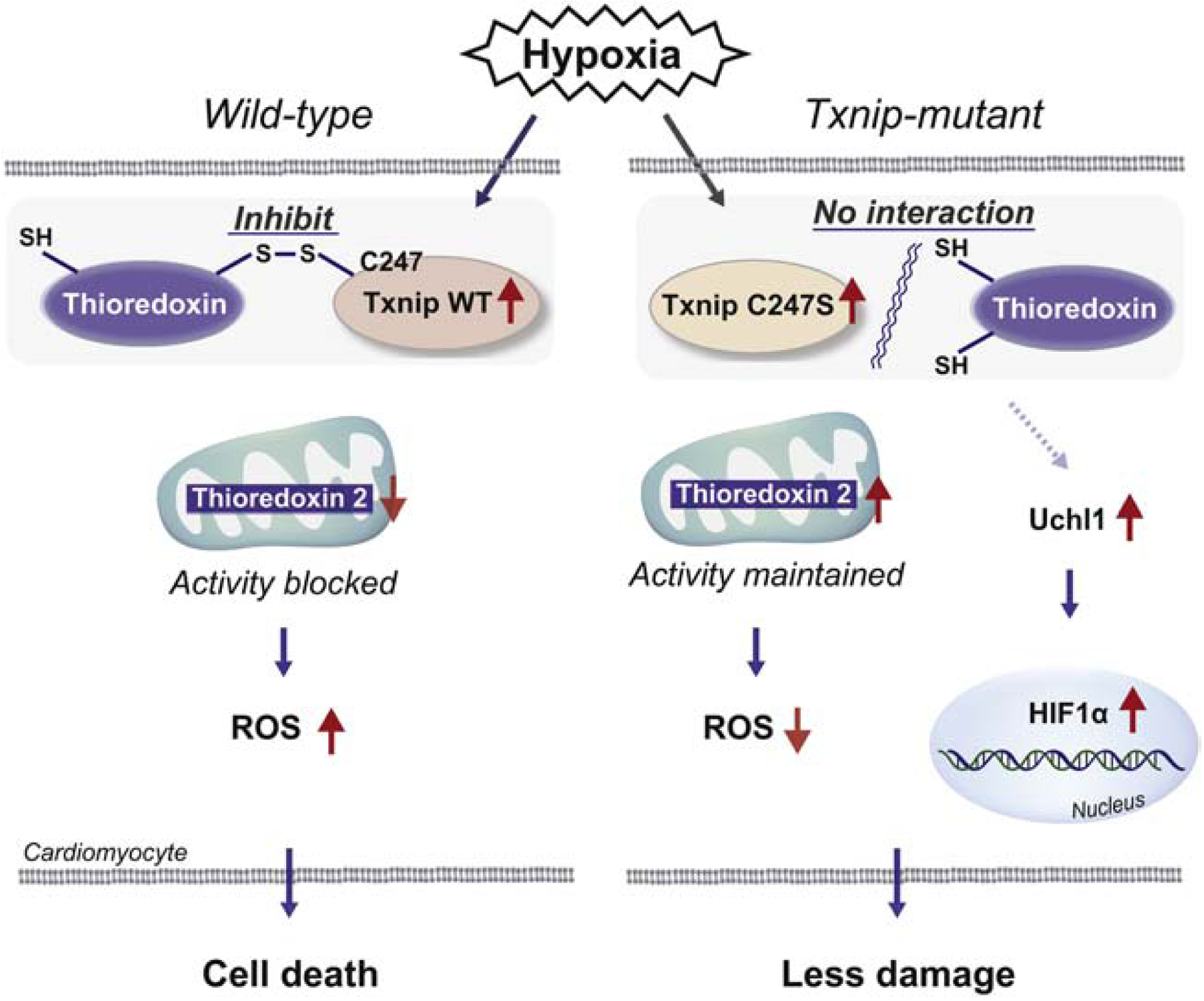
In response to ischemia, Txnip is shuttled into the mitochondria, where Txnip binds to thioredoxin-2 through a disulfide bond formation, resulting in inhibition of anti-oxidant activities and promotion of cardiomyocyte damage in wild type. Txnip C247S fails to form the complex with thioredoxins, thereby increases anti-oxidant activities and protects cardiomyocytes from ischemic insults. Another mechanism involved is activation of the UCHL1-HIF-1 axis, which confers hypoxic tolerance on the Txnip C247S heart.
