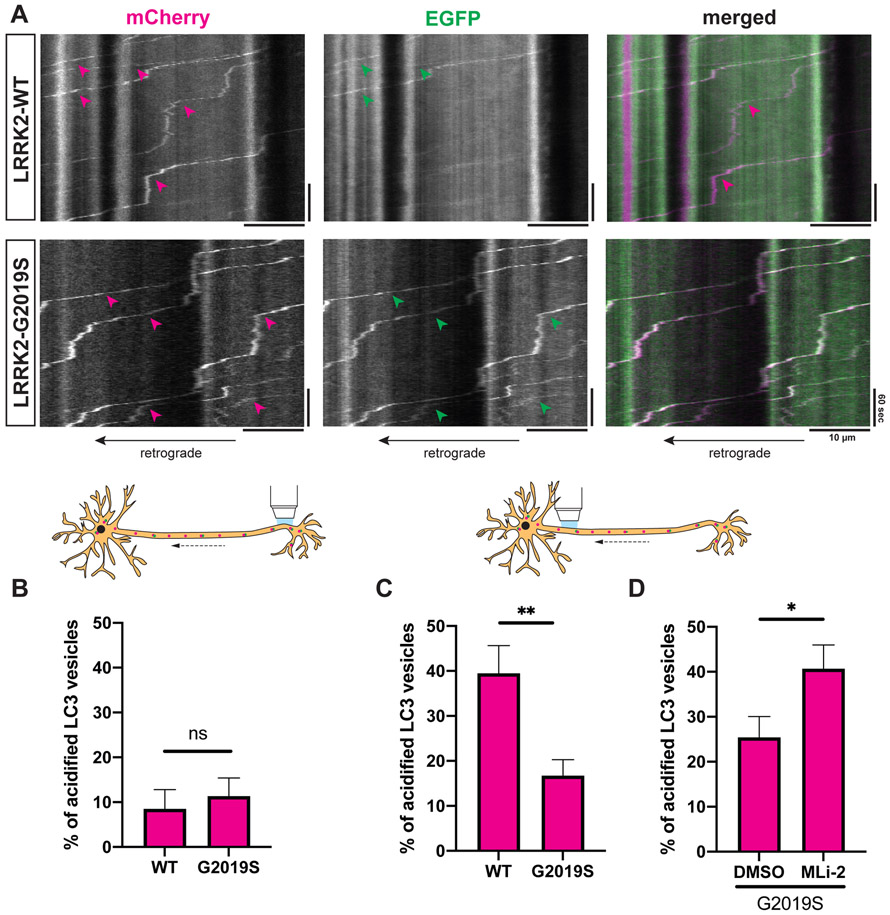
Figure 4. LRRK2-G2019S disrupts acidification of axonal AVs.
(A) Kymographs of mCherry-EGFP-LC3 vesicles in the proximal axon of WT or G2019S KI mouse cortical neurons. Magenta arrowheads: mCherry-positive traces; green arrowheads: EGFP-positive traces; white arrowheads: mCherry- and EGFP-positive traces. (B-D) Percentage of acidified (= mCherry-only positive) AVs in (B) the distal (mean ± SEM; n = 17-20 neurons from 4 independent cultures; ns, not significant, p=0.55; Mann-Whitney test), (C) the proximal axon of WT and G2019S KI neurons (mean ± SEM; n = 29-30 neurons from 4 independent cultures; **p=0.0084; Mann-Whitney test), (D) the proximal axon of G2019S KI neurons treated with DMSO or 100 nM MLi-2 overnight (mean ± SEM; n = 24-26 neurons from 3 independent cultures; *p=0.0123; Mann-Whitney test).
For acidification of axonal LAMP1 vesicles see Figure S5.