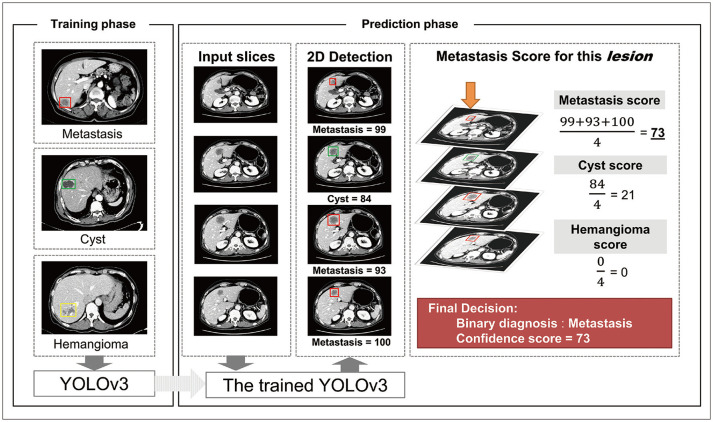
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the DLLD architecture.
The YOLOv3 model was trained in a fully supervised manner using the 3-class CT images of the training cohort and the corresponding labels indicating the class and location of lesions. In the prediction phase, the trained YOLOv3 model finds hepatic focal lesions and predicts information about the detected lesions (location, class, and confidence score for each class) for each CT image in the validation set. Next, an abdominal radiologist manually identifies the lesions that are connected between the adjacent slices, recognizes them as one lesion, and calculates the confidence score for each class using the average of the confidence scores of all slices containing this lesion. If the confidence score of the metastasis is the highest among all classes, the binary classification result of the lesion is “metastasis.” Otherwise, the lesion is considered benign. CT = computed tomography, DLLD = deep learning-based lesion detection algorithm, 2D = two-dimensional