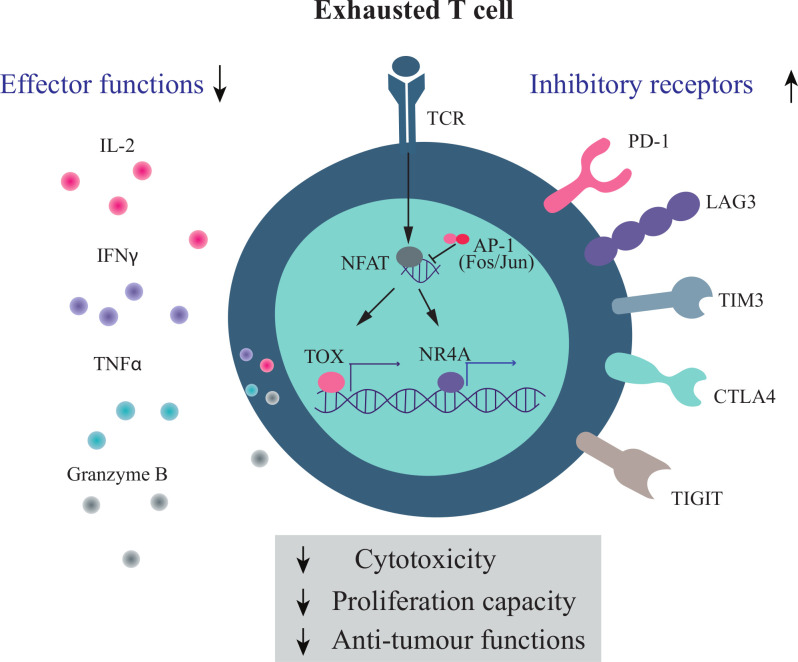
Figure 3.
Markers of T cell exhaustion. T cell dysfunction occurs when there is chronic exposure to antigen, such as in the context of cancer. This loss of function is referred to as T cell exhaustion. T cell exhaustion includes the loss of IL-2 production, decreased proliferative capacity, and reduced cytotoxic abilities, including impairment in granzyme B, IFN-γ and TNF-α production. Along with the loss of functionality, T cells increase the expression of inhibitory receptors such as PD1, LAG3, Tim3, CTLA4, and TIGIT. Some of the key regulators of T cell exhaustion include the transcription factors TOX and NR4A (NR4A1, NR4A2, and NR4A3). IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL-2, interleukin 6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.