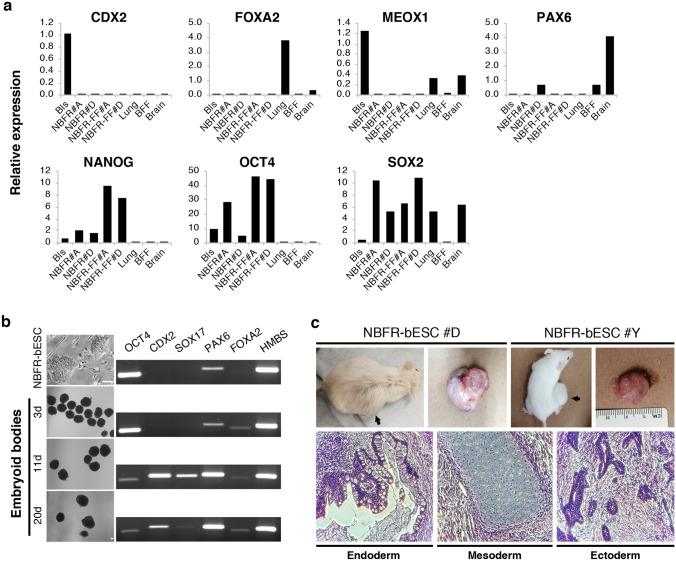
Figure 3.
In vitro and in vivo differentiation of NBFR-bESCs. (a) Gene expression levels of pluripotency (OCT4, SOX2, NANOG), trophectoderm (CDX2), endoderm (FOXA2), ectoderm (PAX6), and mesoderm (MEOX1) markers in representative tissues and two independent NBFR-bESCs lines before (NBFR#A and NBFR#D at passage 10) and after adaptation to feeder-free culture (NBFR-FF #A and #D, passage 10 and 20 after adaptation, respectively). Relative expression was calculated using the comparative CT method (ΔΔCT), normalizing values to HMBS. (b) Bright field images of NBFR-bESCs and embryoid bodies obtained at different times of differentiation. RT-PCR for genes representative of different lineages (OCT4, CDX2, SOX17, PAX6, and FOXA2). HMBS: housekeeping gene. Scale bar 100 μm. (c) Teratomas obtained 12 weeks after injection of two independent NBFR-bESC lines (NBFR #D and #Y) into immunodeficient mouse. Representative histological images showing derivates of the 3 germ lineages. BFF: bovine fetal fibroblasts; Bls: blastocysts, d: days.