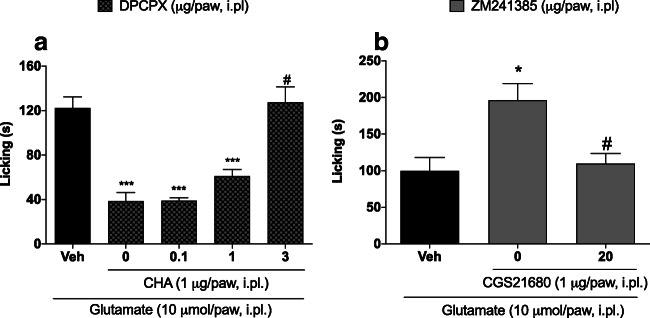
Fig. 4.
Effect of adenosine receptor antagonists administered after adenosine receptor agonists in glutamate-induced nociception. (a) DPCPX—an adenosine A1 antagonist—inhibited the anti-nociceptive effect of CHA. (b) ZM241385—an adenosine A2a antagonist-reduced CGS21680-induced increases in glutamate-induced nociception. DPCPX or ZM241385 was administered by the intraplantar route 5 minutes before CHA or CGS21680, respectively. CHA or CGS21680 was administered by the intraplantar route 5 minutes before glutamate injection. Data are presented as mean±S.E.M. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test. s, seconds. *p<0.05 and ***p<0.001 for comparisons of the effects of agonists and antagonists with those of vehicle. # denotes a statistically significant difference compared with CHA (1 μg/paw) or CGS21680 (1 μg/paw) groups in the absence of DPCPX or ZM241385, respectively. n = 3−5 total male and female mice