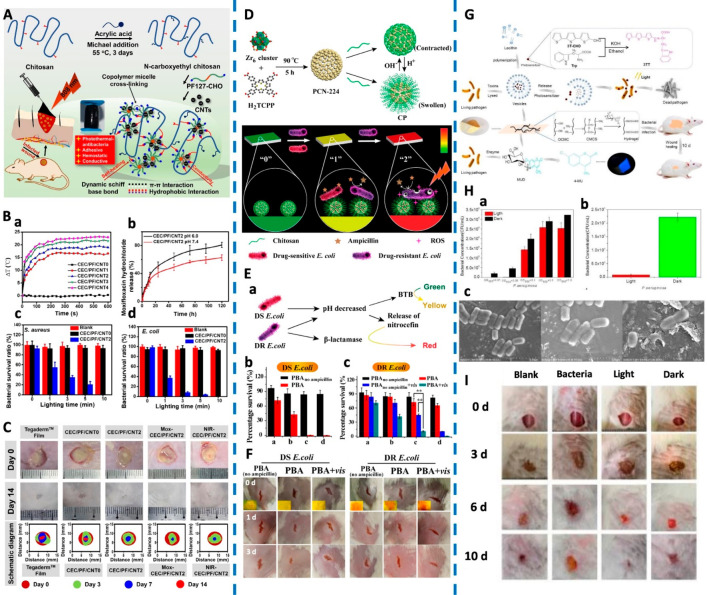
Figure 6.
(A) Schematic of the CEC/PF/CNT hydrogel. (B) Diagrams of ΔT-NIR irradiation time. Drug release behavior. Bacterial survival ratios of S. aureus and E. coli. (C) Representative photographs of a wound infection model with various treatments and the schematic diagram of wound closure on the 3rd, 7th, and 14th day. Reproduced from He et al., 2020.91 Copyright 2020 Elsevier B.V. (D) Schematics of preparation routes of CP- and pH-responsive transformation between contracted state and swollen state of chitosan. Schematic Illustration of PBA (“0”, green) for sensing bacterial infection (“1”, yellow) and drug resistance (“2”, red), and the implementing antibiotic-based chemotherapy and PCN-224-based PDT, respectively. (E) Schematic diagram of PBA for sensing bacterial infection and drug resistance. Viability of DS E. coli and DR E. coli incubated on PBA or PBAno ampicillin with or without light irradiation. (F) Photographs of wounds on the mice. Inset images in the first row revealed the color on PBA. Reproduced from Sun et al., 2020.92 Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society. (G) Schematic of development of an intelligent wound dressing and the mode of action following infection. (H) Vesicle photodynamic against P. aeruginosa. Wound dressing against P. aeruginosa. SEM images of P. aeruginosa after treatments with vesicles containing photosensitizer (Left: P. aeruginosa; Middle: P. aeruginosa with vesicles, in the dark; Right: P. aeruginosa with irradiated vesicles). (I) Photographs of the wound healing model. Reproduced from Zhou et al., 2020.93 Copyright 2020 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, Weinheim.