Figure 2.
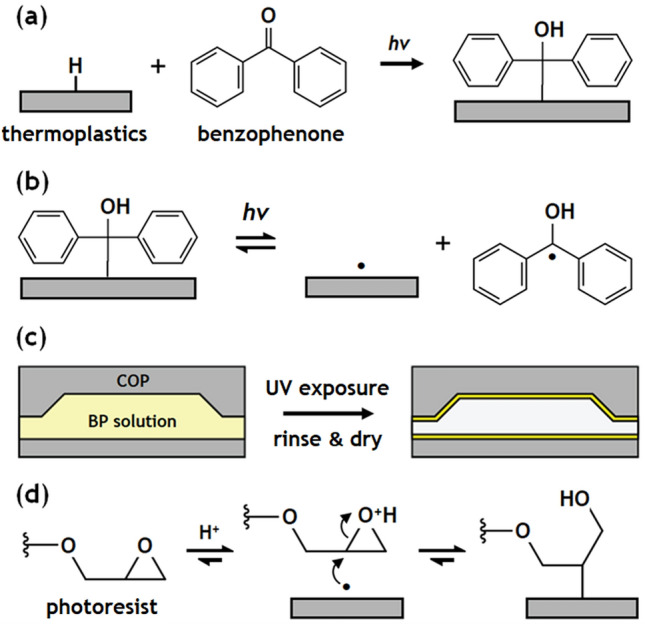
Chemical modification of thermoplastic surface using BP. (a) BP is converted into a semi-benzopinacol or its radical derivatives under UV irradiation, and reacts with thermoplastic polymer which serves as a proton donor. (b) The BP-treated thermoplastic surface may then be photoactivated for covalent bond formation between the surface and an exogenous material upon UV irradiation. (c) A COP microchannel filled with BP solution, and exposed to UV, rinsed, and dried, yielding a photoactive surface before introducing a photoresist in preparation for DLW. (d) Covalent bond formation scenario for the epoxy-based resin. When the laser path coincides with the microchannel surface, free radicals are formed on the COP surface that immediately react with the epoxide ring of the resin, yielding a covalent bond between the resin and thermoplastic surface.
