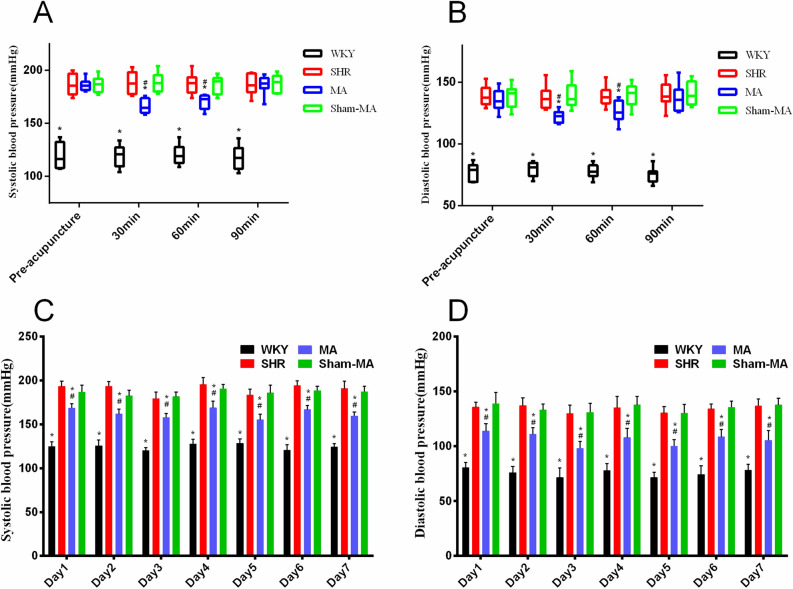
Figure 1.
Reducing blood pressure (BP) effects induced by MA in SHRs. Differences in systolic blood pressure (SBP) (A) (H(Pre-acupuncture) = 17.48, H(30 min) = 25.68, H(60 min) = 24.15, H(90 min) = 17.48, Kruskal–Wallis Test) and (C) (F(Day1) = 102.21, F(Day2) = 101.11, F(Day3) = 100.12, F(Day4) = 103.36, F(Day5) = 102.56, F(Day6) = 108.47, F(Day7) = 100.04, repeated measurement ANOVA) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (B) (H(Pre-acupuncture) = 17.79, H(30 min) = 25.32, H(60 min) = 21.78, H(90 min) = 18.12, Kruskal–Wallis Test) and (D) (F(Day1) = 96.62, F(Day2) = 97.40, F(Day3) = 94.67, F(Day4) = 95.72, F(Day5) = 94.99, F(Day6) = 98.54, F(Day7) = 93.61, repeated measurement ANOVA) among WKY, SHR, MA and Sham-MA groups were detected at 30, 60 and 90 min after the first day of treatment, or every day of the 7-day treatment. *p < 0.05 versus the SHR group, #p < 0.05 versus the Sham-MA group.