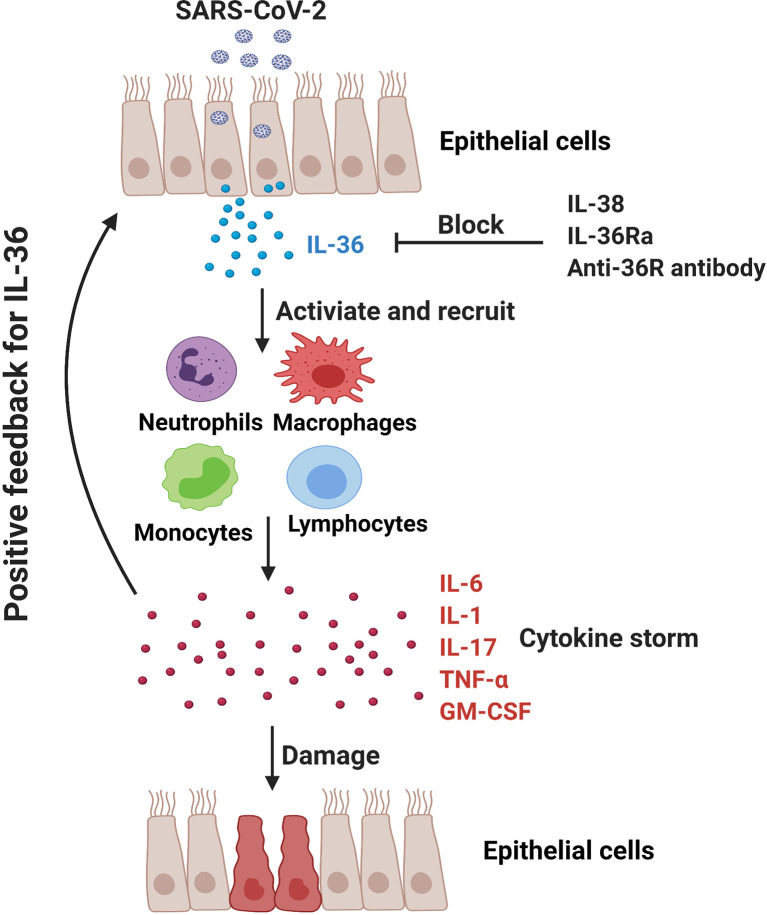
Figure 2.
In COVID-19 patients, SARS-CoV-2 may promote hyperinflammation in the lung and exacerbate tissue damage. IL-36-activated inflammatory immune cells (e.g., monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils and pathogenic T cells) produce IL-6, IL-1, IL-17, TNF-α and GM-CSF to further amplify IL-36 responses. IL-36Ra and IL-38, as the natural antagonistic mediators in IL-36 family might be a promising therapeutic target for COVID-19 via inhibiting IL-36 signaling pathway and alleviating pulmonary hyperinflammation.