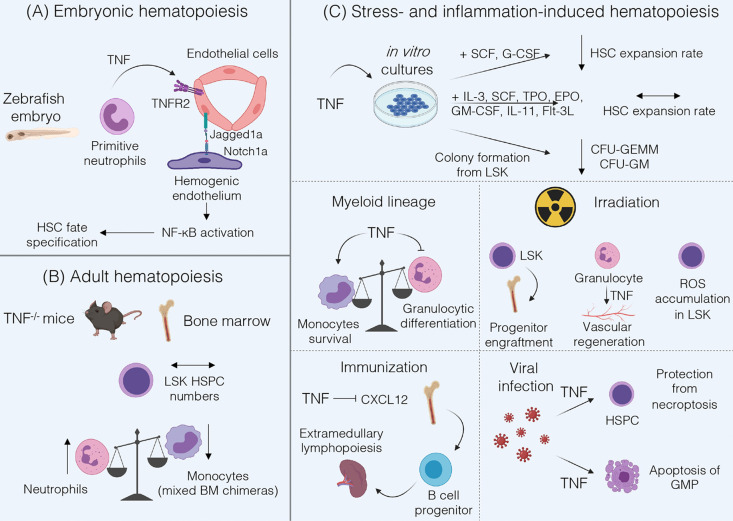
Figure 1.
Summary of TNF functions in hematopoiesis. (A) During fetal hematopoiesis in zebrafish TNF/TNFR2 signaling is required to establish HSC fate via activation of Notch and NF-kB signaling (18). (B) Bone marrow of adult TNF-deficient mice is characterized by normal LSK HSPC numbers and by an increase in Gr-1+ neutrophils (19). Mixed Tnf -/- and Tnf +/+ BM chimeras underrepresent TNF-deficient monocytes (20). (C) TNF may inhibit HSC expansion when cultured with SCF and G-CSF, but not in cytokine-rich medium (21). Addition of TNF to LSK cultures inhibits formation of CFU-GEMM and CFU-GM (22). TNF promotes monocytes survival (20) and inhibits proliferation and differentiation of granulocyte progenitors (19, 23, 24). Under inflammatory conditions induced by irradiation TNF may be beneficial for progenitor engraftment (25) but stromal cell-derived TNF induces ROS accumulation in HSPCs (26), and granulocyte-derived TNF is involved in vascular regeneration (27). Following immunization, TNF may suppress CXCL12-dependent retention of B cell progenitors in the bone marrow leading to their migration (28). In the case of viral infections TNF protects HSPCs from necroptosis, enhances myelopoiesis and induces apoptosis of GMP (21).