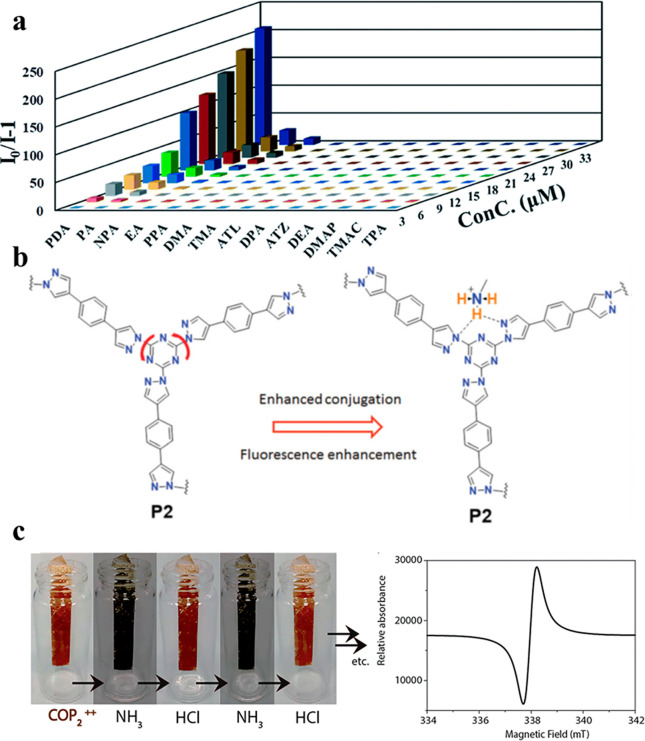
Figure 9.
(a) Stern–Volmer plots of 14 different amines tested as analytes for F-CTF-3. PDA = p-phenylenediamine; PA = phenylamine; NPA = 1-naphthylamine; EA = ethylamine; PPA = n-propylamine; DMA = dimethylamine; TMA = trimethylamine; ATL = amitrole; DPA = diphenylamine; ATZ = 5-amino-1H-tetrazol; DEA = diethylamine; DMAP = 4-dimethylaminopyridine; TMAC = tetramethylammonium chloride; TPA = triphenylamine. Reproduced from ref (112) with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry. Copyright 2020. (b) Sensing mechanism between protonated aliphatic amines and pyrazole rings of P2 leads to conjugation enhancement and turns on the fluorescence signal. Reproduced from ref (115) with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry. Copyright 2020. (c) Reversibility of NH3 sensing with COP2++. Sorption of NH3 induces the formation of radical cationic viologen species in the COP, as demonstrated by an EPR spectrum. Reproduced from ref (109) with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry. Copyright 2016.