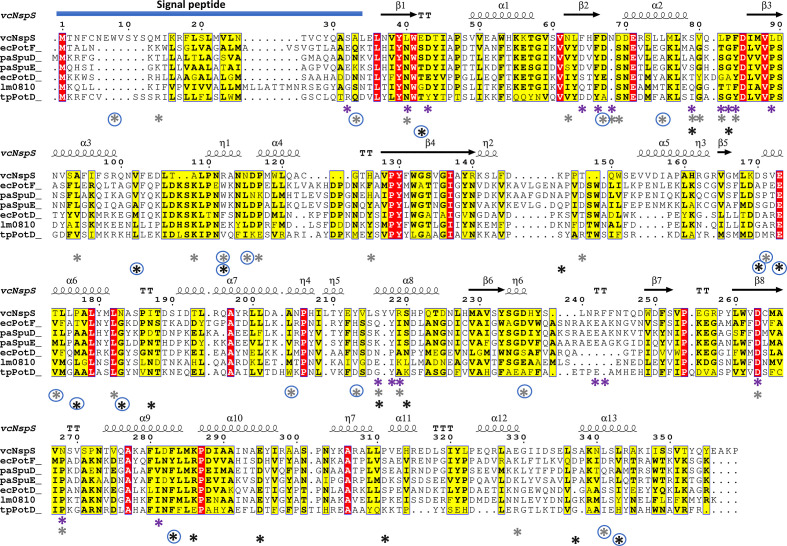
Fig. 4.
Multiple sequence alignment of NspS from V. cholerae and homologues. NspS homologues with 3D crystal structures in the Protein Data Bank were selected and the secondary structure at the top of the alignment is based on the closed conformation NspS homology model. Sequences were aligned with Clustal Omega and the figure was produced using ESPRIPT. Red highlighted residues are completely conserved and yellow residues share some sequence similarity. The following structures were used for the alignment: ecPotF (putrescine receptor from E. coli ; PDB ID: 1A99), paSpuD (polyamine receptor from P. aeruginosa ; PDB ID: 3TTM), paSpuE (polyamine receptor from P. aeruginosa ; PDB ID: 3TTN), ecPotD (spermidine/putrescine transporter from E. coli ; PDB ID: 1POT), lm0810 (spermidine/putrescine transporter from Listeria monocytogenes ; PDB ID: 4GL0), tpPotD (putrescine/spermidine transporter from Trepomena pallidum; PDB ID: 2V84). The signal peptide region of the sequence is indicated with a blue bar at the N-terminus of the protein sequences. Coloured asterisks below the sequence alignment indicate missense mutation locations. Purple asterisks identify residues changed for single-missense mutations, grey asterisks are for double-missense mutations, and black asterisks indicate triple- and quadruple-missense mutations. Blue circles surrounding asterisks indicate residues mutated in multiple-missense clones that do not contain sites of single-missense mutants.