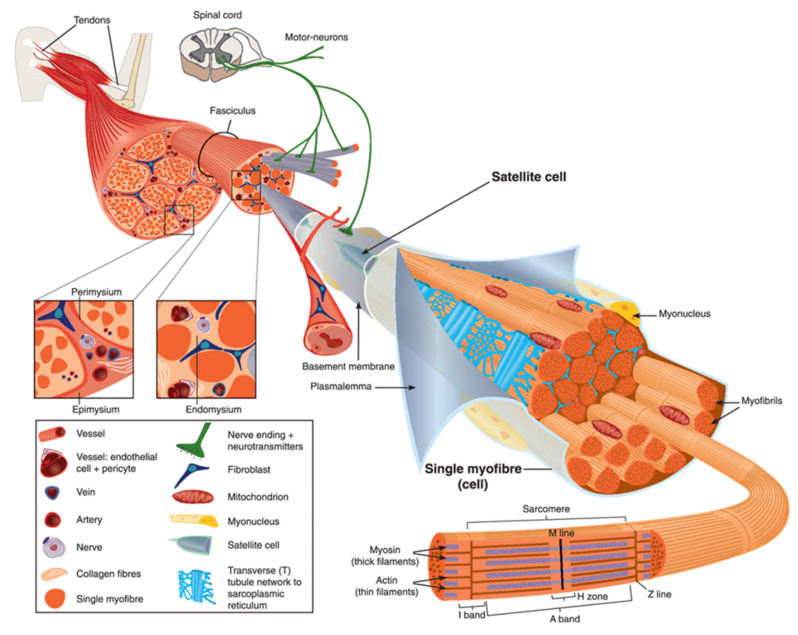
Figure 1.
Scheme of skeletal muscle and associated structures. (Left-hand part) Epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium constitute three connective tissue layers that form the lattice network and associated basement membranes in which myofibers regenerate after injury. The epimysium is the outer layer that surrounds the entire muscle and is contiguous with the tendon and endosteum (fascia surrounding bone). The perimysium surrounds bundles of myofibers. The endomysium is located between individual muscle fibers. (Right-hand part) Satellite cells are located between basement membrane and sarcolemma. Sarcolemma bounds each myofiber, which is composed by multiple nuclei and the sarcoplasm that contains mitochondria, sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils. The myofibril is the contractile unit of a myofiber. Specialized cytoskeleton within the myofibril forms repeated structures, called sarcomeres, which appear as a succession of light and dark bands under polarized light optical microscopy. The sarcoplasmic reticulum is the major provider of Ca2+ required for muscle contraction. It is connected to transverse tubules that surround sarcomeres. Adapted from Reference [15] with the Permission 5036470714502 from John Wiley and sons.