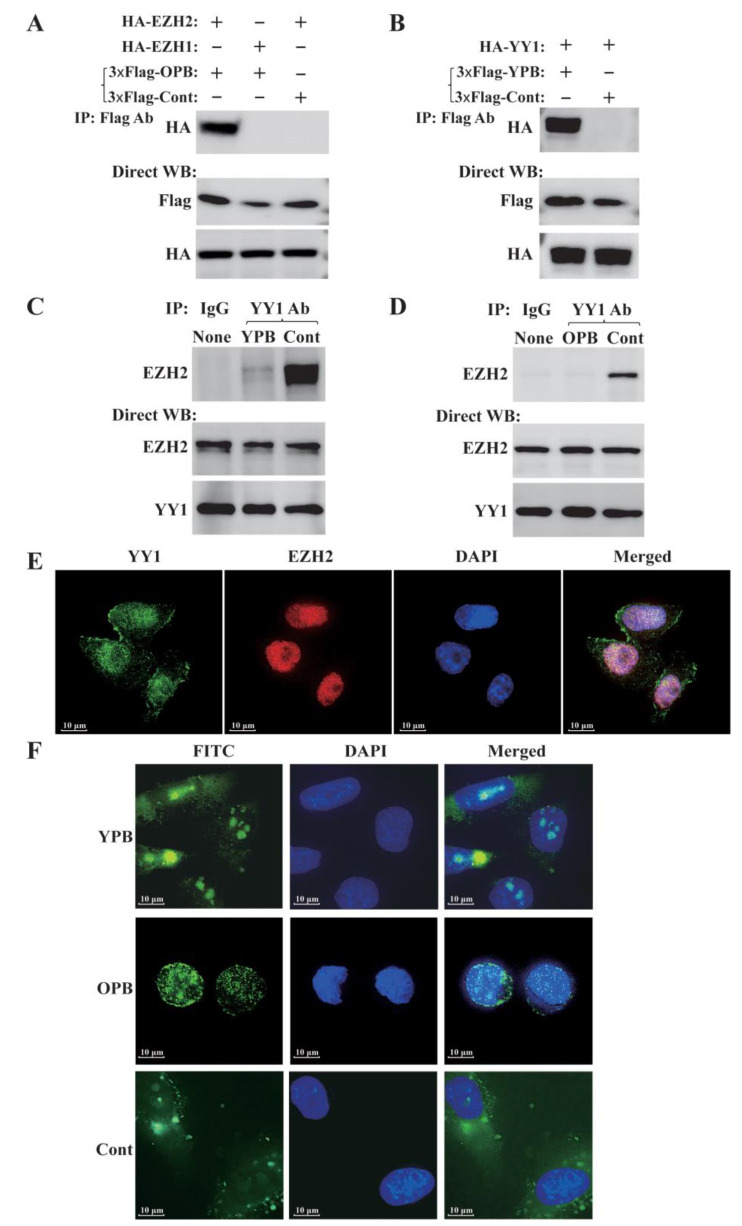
Figure 4.
Examination of YPB and OPB peptides in blocking YY1-EZH2 interaction, and their subcellular localization. (A,B) Co-IP experiments to determine OPB and YPB interaction with EZH2 and YY1, respectively. In A, 3×Flag-OPB-2A1-EGFP, 3×Flag-Cont-2A1-EGFP expression vectors, and an empty vector were individually cotransfected with HA-EZH2, HA-EZH1 expression vectors, or an empty vector. Cell lysates were co-IPed using Flag antibody followed by Western blot analysis using HA antibody. In B, similar to A but using 3×Flag-YPB-2A1-EGFP and HA-YY1 in the transfection and co-IP studies. (C,D) Examination of YPB and OPB peptides’ effects on YY1-EZH2 interaction. MDA-MB-231 cell lysates were treated by 30 μM of Cont, OPB, and YPB peptides for 4 h, followed by co-IP using 2 µg of normal IgG, YY1, and EZH2 antibodies. The co-IPed samples were analyzed by Western blot using YY1 and EZH2 antibodies to evaluate the effects of YPB (C) and OPB (D) peptides on YY1-EZH2 interaction. (E) Examination of YY1 and EZH2 colocalization in cells. MDA-MB-231 cells were immunostained by YY1 and EZH2 antibodies. DAPI was used to visualize nuclei. (F) Detection of subcellular localization of peptides. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated by 30 μM of Cont, OPB, and YPB peptides for 48 h, followed by DAPI staining. The peptides were all N-terminal FITC-labeled and thus could emit green fluorescence.