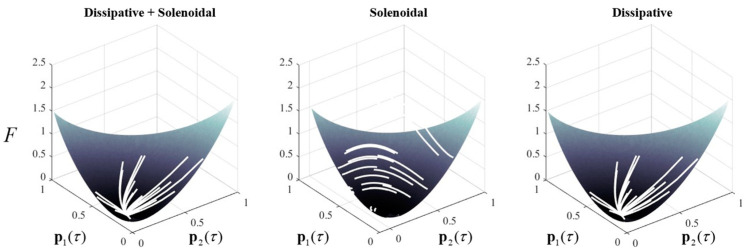
Figure 1.
Solenoidal and dissipative dynamics in categorical systems. This figure provides a numerical example of a (three-dimensional) system consistent with Equation (5), and its decomposition as in Equation (6), starting from a series of random initial states. Each trajectory is shown in white. In addition, it illustrates the free energy landscape (in 2 dimensions) to demonstrate the interpretation given in Equation (7). On the left, we see the combination of the dissipative and solenoidal flows that tend towards the free energy minimum. In the centre, the dissipative part of the flow has been suppressed, leading to trajectories around the free energy contours. Such trajectories conserve free energy (but not probability) so do not find its minimum. On the right, the purely dissipative trajectories find the free energy minimum, but take subtly different paths compared to those supplemented with the solenoidal flow.