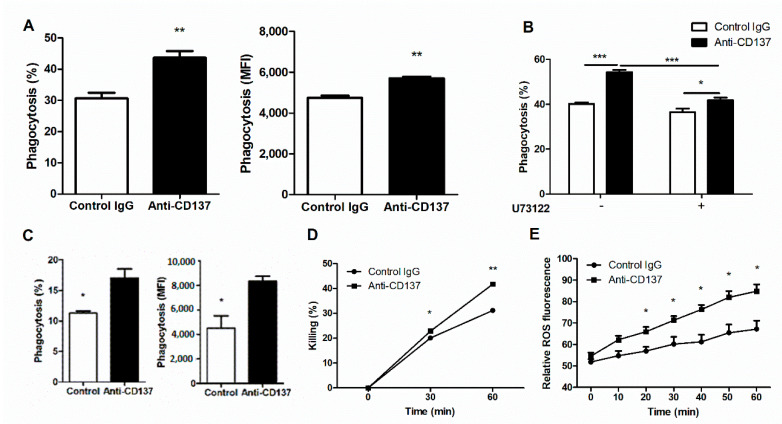
Figure 4.
CD137 stimulation enhances the phagocytic and fungicidal activities of neutrophils. (A) In vitro analysis of phagocytosis. Purified neutrophils were preincubated with anti-CD137 mAb (5 µg/mL) for 1 h and challenged with opsonized, FITC-labeled HK C. albiccans (MOI = 10) for 20 min. The percentages and MFIs of FITC-positive neutrophils were presented for the extent of phagocytosis (n = 5 mice per group). (B) Neutrophils were pretreated with 2 μM U73122 (PLC inhibitor) 2 h before antibody treatment. The percentages of FITC-positive neutrophils were calculated using FACS. (C) In vivo analysis of phagocytosis. WT mice were intraperitoneally injected with 200 μg of anti-CD137 or control rat IgG antibody 1 h before challenge with FITC-labeled HK C. albicans. Cells harvested from the peritoneum were stained and percentages of phagocytosis were determined by counting CD11b+Ly6Ghi neutrophils containing C. albicans. The MFIs was also presented for the extent of phagocytosis (n = 5 mice per group). (D) Fungicidal assays for neutrophils primed with anti-CD137 or control antibody. (E) Measurement of ROS in neutrophils primed with anti-CD137 or control antibody. Results are representative of 3 experiments (n = 3 per group). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 between the two groups or between the indicated groups.