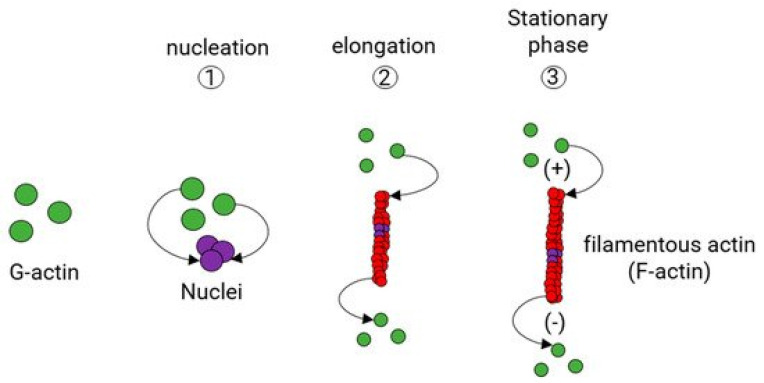
Figure 3.
Actin treadmilling mechanism. Actin elongation and breakdown are contingent upon ATP levels; in f-actin elongation, g-monomers are “charged” (ATP rather than ADP + Pi) and are added to the positive (+) end. As it treadmills down towards the positive end, ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP + Pi, becomes unstable, and susceptible to cleavage proteins.