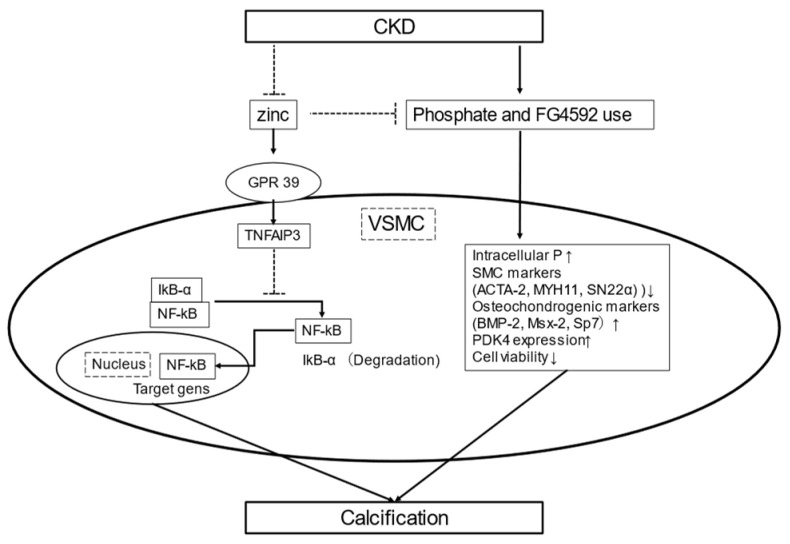
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of zinc and calcification. CKD induces hypozincemia and hyperphosphatemia. Zinc supplementation may increase zinc finger protein TNFAIP3 levels by upregulating zinc-sensing receptor ZnR/GPR39-dependent TNFAIP3 gene expression. Increased TNFAIP3 inhibits NF-kB activation and osteo-/chondrogenic reprograming, resulting in suppression of phosphate-induced VSMC calcification [17]. FG4592, an orally bioavailable PHI, promotes phosphate uptake in VSMCs and phosphate-induced loss of smooth muscle cell markers (ACTA-2, MYH11, SM22a) and also enhances osteochondrogenic gene expression (Msx-2, BMP-2, Sp7). Zinc inhibits FG4592-aggravated calcification caused by high phosphate by maintaining the VSMC phenotype, decreasing phosphate uptake, and lowering osteochondrogenic gene expression and levels of PDK4, as well as preserving Runx2 phosphorylation and cell variability [16]. Abbreviations: ACTA-2, smooth muscle a-2 actin; BMP-2, bone morphogenic protein-2; CKD, chronic kidney disease; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B; Msx-2, Msh Homeobox 2; MYH11, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain 11; PDK4, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4, PHI, prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors; Runx2, runt-related transcription factor 2; TNFAIP3, TNFa-induced protein 3; VSMCs; vasculature smooth muscle cells.